为了保证监控系统中摄像机、镜头工作的可靠性,延长其使用寿命,必须给摄像机装配具有多种特殊性保护措施的外罩,称为防护罩。除此之外,防护罩还可以尽量防止对摄像机和镜头的人为破坏。防护罩按照使用地点的不同可分为室内型和室外型。 室内防护罩 室内防护罩必须能够保护摄像机和镜头,使其免受灰尘、杂质和腐蚀性气体的污染,同时要能够配合安装地点达到防破坏的目的。室内护罩一般使用涂漆或经阳极氧化处理的铝材、涂漆钢材、黄铜或塑料制成,如果使用塑料,应当使用耐火型或阻燃型。防护罩必须有足够的强度,安装界面必须牢固,视窗应该是清晰透明的安全玻璃或塑料(聚碳酸酯)。电气连接口的设计位置应该便于安装和维护。 摄像机工作温度为-5℃~45℃,而最合适的温度是0℃~30℃,否则会影响图像质量,甚至损坏摄像机。因此室外型防护罩要适应各种气候条件,如风、雨、雪、霜、低温、曝晒、沙尘等。室外型防护罩会因使用地点的不同配置如遮阳罩、内装/外装风扇、加热器/除霜器、雨刷器、清洗器等辅助设备。 室外防护罩 首先,室外防护罩密封性要高,以避免雨水进入。同时进线口要开在防护罩的下方,避免雨水顺线缆倒流入防护罩。在防护罩前方还应安装雨刷,以便及时清理所积雨水和污垢,使摄像机能通过玻璃,摄取清晰的图像。罩前或玻璃上除霜器,在视窗积霜、积雪时将其融化。 其次,防护罩内应装有加热器,在温度较低的环境中进行加热,提升防护罩内部温度,确保摄像机/镜头正常工作;内装或外装风扇可以使罩内空气流通,降低防护罩内的温度;在多风沙少雨水的地点还要考虑配置清洗器,以便和雨刷器配合随时对视窗玻璃进行清洁,保证图像监视效果。 室外型防护罩的辅助设备控制功能有自动控制和手动控制两种,像加热器/除霜器、风扇都是由防护罩内部的温度传感器自动启动或关闭的,而像雨刷器、清洗器等动作是由控制人员通过对控制设备的操作来实现的。 室外护罩一般使用铝材、带涂层的钢材、不锈钢或可以使用在室外环境的塑料制造。制造材料必须能够耐受紫外线的照射,否则回很快出现裂纹、褪色、强度降低等老化现象。在需要护罩耐用、具有高安全度、可抵抗人为破坏的环境中应该使用不锈钢护罩;经过适当处理的铝护罩也是一种性能优良的护罩,处理方法有三种:聚氨酯烤漆、阳极氧化、阳极氧化加涂漆。在有腐蚀性气体的环境中不应该选择铝制或钢制互助;在盐雾环境中应使用不锈钢或特殊塑料制成的护罩。另外为增加防护罩的安全性能,防止人为破坏,很多防护罩上还装有防拆开关,一旦防护罩被打开将发出报警信号。监控系统中的防护罩种类繁多,一般可按照其形状分为矩形护罩、墙壁或天花板用护罩、球型护罩、角装护罩、坡形护罩等。
不锈钢导轨防护罩的特点: 1、不锈钢导轨防护罩具有密封好,能防铁屑、防冷却液,防工具的偶然事故。坚固耐用,运行平稳,噪音小,外形美观。可对机床生产厂带来完美外观。是机床不可缺少之零件。 2.不锈钢导轨防护罩适宜高速运动机床导轨防护既平稳又无振动噪音。 3.不锈钢导轨防护罩不但保护机床导轨的使用寿命,更重要的是保证了机床精密度。 4.不锈钢导轨防护罩每一节护板同时平行拉开,并同时平行缩回,运行自如。 5.不锈钢导轨防护罩不会使机床导轨脱节,没有撞击声,既美观又提高了机床导轨的使用寿命。 6不锈钢导轨防护罩在原密封胶条的基础上又加盖了一层不锈钢盖板,防止铁屑高温烧伤胶条擦入轨面拉伤机床导轨。
领导吩咐给实验室的GC-MS、原子吸收等大型仪器做个防护罩,找了很久没找到很合适的公司。请问大家的仪器防护罩是什么类型的,有没得合适的公司推荐?本人重庆的,谢谢!
各位老师好,我现在遇到了一个难题,希望大家帮助一下:我的公司有台拉伸试验机,是液压的,公司常进的原材料都是一些热轧板,所以经常要做弯曲试验,因为压辊不是很多,所以用大一点的压辊,然后再用压缩试验的压板平压一下。我们新盖的实验室四面都是玻璃,没有墙,如果试样要是跑出去的话就会把玻璃打碎,所以想做一个防护罩,看看大家有没有做的,传上照片看一下。谢谢。
一:概述,Wh-01 型高密封引风涡流防护罩,主要应用世界先进的涡流引风技术,大大的降低了防护罩内的温度,同时自动除尘前罩免维护。主要应用与一些特殊场合的监控,例如:室内汽包水位监控,大型高温监控场所,室外环境恶劣场所的监控,较本公司推出的Wh-01在性能上增加了免清洗免维护的功能,大大了降低了维护费用,增加了产品的使用的寿命。本产品拥有个人专利,在电厂,化工厂,各种工业控制中广泛应用。产品整体设计新颖实用,采用最基本的机械原理实现复杂控制动作,应用双层结构设计,通过隔离散温,涡轮降温,大大的提高了防护罩的密封性和冷却性。Wh-01型高密封引风涡流防护罩,集国内外防护罩的优势,根据石油、化工、电力、冶金、轻工等部门建议和要求而进行优化设计的新型产品,护罩材料采用长寿命,耐腐蚀的特殊材料,内部装置,采用世界先进技术涡流引风技术,降温速度快,可靠性强。与目前国内外生产和使用的同类产品相比具有显示耐高温,免清洗,免维护,结构新颖,可靠性强,安装方便。根据电厂现场的建议而改进的内部电路更趋合理,外型愈加美观的新产品。此产品推出后受到广大用户及设计人员的普遍欢迎和广泛选用。二:工作原理:涡流引风装置是一种针对西北地区风沙大温度高而专门设计的新型防护罩,采用双层设计结构,密封性强,散热冷却效果好,中间利用简单的机械原理将摄像机加紧固定,后置散热,夹层管道利用新型技术涡流引风,将气体导入加速,在某一特定区间内迅速加压提速,以雾化的效果高速喷射在特殊材料的镜片上,以达到镜片的清洗。三:使用与安装:防护罩的设计是根据通用摄像机量身定制,并且有一定装置供不同型号摄像机移动。线材孔均采用国家标号视频线,电源线。安装时,外面护罩上有四个凹槽,可以通过悬空的方式安装,也可以通过地下的底座固定在支架上。

[align=center][size=16px][b]流化床在线设备改造[/b][/size][/align]常规的顶喷式制粒流化床的主要组成系统分为温度控制系统、喷雾系统以及其他控制系统等。主要的结构有底锅、喷嘴、空气进出口、滤袋、取样口等,需要调整的工艺参数比较少,因此操作比较简单。在制粒过程中,粘合剂在蠕动泵和压缩空气的作用下经过喷嘴喷到处于流化状态的物料上,使得粉末在粘合剂的作用下和周围粉末聚并成粒子核,粒子核与粒子核之间慢慢形成比较大的颗粒。继续向流化床内部喷入粘合剂,使得颗粒和颗粒之间,颗粒与粒子核之间发生聚并作用形成更大的颗粒。同样,粘合剂喷入量过少,在进风量和温度等工艺参数的影响下,聚并的颗粒也会破碎,变成小颗粒和小的粒子核。颗粒生长过程如下。[img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031750279617_8904_3890113_3.jpeg[/img]本实验采用的是山东新马制药装备有限公司的实验型流化床(LGL 002),设备实物图如上图。此流化床设备操作简单方便,但是缺乏信息采集装置,不能及时准确地得到颗粒的水分含量,而且制粒过程中需要进行操作的实时工艺参数数据也不能够及时记录,这样就无法对每一时刻的工艺参数数据与颗粒的水分含量进行关联分析,影响颗粒水分含量的关键工艺参数不能掌握,对制粒工艺也就不能有更为充分的理解。为了及时获取相关的颗粒水分信息和工艺参数信息,需要对流化床进行改造。安装[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url]为了获得流化床制粒过程中颗粒的实时水分数据,需要在流化床设备上添加[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url]用于实时在线获取颗粒的[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]数据。NIRS在线分析光谱采集方式主要有接触式和非接触式两种,非接触式主要通过从流化床的视镜进行对颗粒的采谱,接触式是将近红外探头安装到流化床底锅内部,直接与颗粒接触进行采谱。本文选用微型[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url](MicroNIR PAT-U)在流化床制粒过程中采集颗粒的光谱数据进行水分含量的在线监测。与传统的近红外仪器相比,MicroNIR PAT-U体积较小、方便携带、质量较轻,对生产过程不会产生太大影响,因此在实际生产中适合用来对颗粒进行监测。温度对近红外仪器具有较显著的影响[50],同一个仪器在不同的温度条件下采集到的光谱也会所差异。流化床内温度比较高,并且随着实验过程物料温度在不断变化,如果直接将近红外探头与物料进行接触,采集到的光谱会有较大的误差,对实验结果的准确性也会产生影响。因此,为了尽可能地减少温度对近红外仪器的影响,将MicroNIR PAT-U外接探头,让近红外仪器不与物料直接接触,从而可以采集到较为稳定和准确的光谱数据。MicroNIR PAT-U与探头的连接方式为螺纹连接,在距离探头顶端与底锅厚度相同的地方安装材料为聚四氟乙烯的密封圈,保证采集光谱过程中的密封性与可靠性。MicroNIR PAT-U和探头的整体安装图如下图所示。为了采集颗粒的光谱,要将近红外探头伸入流化床内部,这就需要在流化床的底锅上进行打孔,孔的直径要比探头的直径大0.2~0.3mm,使得生产过程中探头不会发生晃动,保证光谱采集位置的一致性。孔的位置要尽量与取样口保持在同一条水平线上,这样可以减小近红外仪器采集的光谱数据与物料离线测量的数据在外部环境条件下的差异,尽可能减少采集数据的误差。探头具体的安装位置如下图所示。近红外探头吹扫装置在物料未成粒之前,粉末状的物料具有很强的粘附性,随着实验的进行,粉末会粘附在近红外探头上,从而对光谱的正确性产生严重的影响。这就要求在制粒过程中及时地清除掉粘附在探头上的粉末以消除这种不利影响。然而,频繁地把探头拿出来手动擦净不但会影响探头地使用寿命,而且由于光谱地采集是一个连续的过程,这样做反而会更加影响光谱数据的准确性。因此,流化床上安装近红外探头吹扫装置是非常有必要的。上节已经提到,近红外探头伸入流化床的长度与底锅的厚度一样,因此,近红外探头与底锅内壁是平行的。在近红外探头孔内径的下方孔壁上开一个直径为5mm的小孔,设计一个端部带螺纹的空心装置,外部接上吹入压缩空气的橡胶管,用于在制粒过程中对探头的吹扫,使物料尽量少的粘附在探头上。吹扫装置的原理示意图及安装实物图如图所示。吹扫装置要设置适当的吹扫频率和吹扫时间,并不是频率越快、时间越长越好。吹扫频率太快,每次吹扫时间过长,可能在探头采集光谱的时间段,刚好物料被吹扫装置吹跑,使得近红外探头实际采集的为空气的光谱,这会对结果造成较大的误差。近红外探头采集光谱的时间大约在2s左右,因此设置吹扫装置的脉冲频率设置在15s吹一次,每次吹1s为最适宜频率。工艺参数采集装置流化床制粒过程中使用的工艺参数比较少,因此每个工艺参数都对颗粒质量属性产生重要的影响。在制粒过程中,流化床的主要工艺参数有雾化压力、蠕动泵流量、进风温度、排风温度、进风量和物料温度。为了获取这些工艺参数数据,需要在流化床的相应位置上安装风量传感器、温度传感器、流速计、压力表等。流化床工艺参数采集装置的原理示意图如下图所示。进风温度、排风温度、风量的传感器,流量计和压力表都是安装在流化床系统内部,只有物料温度传感器需要在制粒的过程中将传感器加入到流化床内部。物料温度传感器采用热电偶式,为了测量流化床制粒过程中物料的温度,也需要在底锅上进行打孔,使温度传感器伸入到流化床内部,通过与物料直接接触的方式感受物料的温度并转换成可用于输出的信号。传感器孔的位置尽可能与近红外测量的位置在同一水平线上,保证测量的物料温度与近红外探头测量的物料是同一状态下的。物料温度传感器如下图所示。 [img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031750281516_7229_3890113_3.png[/img][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031750284280_7065_3890113_3.png[/img]物料温度传感器暴露在外部,容易受外部环境的影响。为了确保传感器的稳定性和可靠性,保证在制粒过程中传感器不会发生晃动,需要对物料温度传感器增加固定装置。采用管夹作为温度传感器的增固装置,如上图所示。
[align=center][size=16px][b]流化床制粒[/b][/size][size=16px][b]发展现状[/b][/size][/align]药品是人们常备的不可或缺的日常用品。近年来,随着国民生活水平的提高,人们对药品质量和药物安全问题广泛关注,制药领域也随之越来越多的进入到我们的视野中。长期以来,制药行业都采用传统的方式进行生产,无论是自动化、信息化水平还是认知观念水平都与其他行业存在着一定的差距。“十三五”规划以来,国家大力发展智能制造,制药行业作为制造业的一部分,需要紧跟发展潮流,朝着信息化、智能化方向发展。固体制剂是目前最常见的剂种之一,其生产过程是将原料通过一系列操作包括粉碎、混合、制粒、包衣及压片等过程转化成药物制剂。无论是制作胶囊还是压片,制粒都是非常重要的关键步骤。制粒是将药物粉末与相关的辅料进行混合,待混合均匀后再喷入润湿剂或者粘合剂,在设备中制成具有颗粒形态的过程。干法制粒和湿法制粒是目前固体制粒中最常用的两种方法[font='calibri'][size=13px][1][/size][/font]。干法制粒不需要使用粘合剂,常用于对水分比较敏感的制剂;湿法制粒是常用的制粒方法,在混合均匀的粉末中喷入粘合剂,将粉末表面打湿,粉末通过粘合剂的媒介作用聚结在一起可以慢慢形成颗粒。流化床制粒是常见的湿法制粒方法之一。流化床制粒过程中使用的工艺参数较少、且操作方法简单,广泛应用于固体制粒中。然而,目前的流化床制粒大多依靠于人工经验,对于制粒过程中颗粒的质量属性的变化都是离线进行分析,严重滞后于生产过程。制粒过程信息不透明,对制粒过程影响因素不能准确把握,容易导致药物疗效达不到预期甚至造成制粒批次的失败。随着计算机信息技术、人工智能、传感器技术的发展,及时获取流化床制粒过程工艺参数与颗粒的关键质量属性,通过数据挖掘出工艺参数变化对于流化床制粒过程的影响,通过质量属性的变化及时调整工艺参数,从而可以大大提高制粒成功率,打破国外技术封锁,实现连续化、智能化生产的目标。针对流化床制粒信息化、自动化水平低,数据采集困难等问题,合理改造设备以及通过机器学习等人工智能算法了解工艺参数的内部机理,达到准确调控,对流化床制粒连续化、智能化生产具有重要指导意义。流化床制粒技术只在一个腔体中就可以完成整个制粒过程。药物粉末和辅料等一次性的投入到密封的腔体中,在腔体内进行混合,直至腔体内的各种物料都混合均匀,接着从底部通入热空气,药物粉末在从下方而来的热空气作用下能够保持悬浮,从而达到理想的流化状态。接着将按照一定比例配成的黏合剂液体在蠕动泵和一定压力的压缩空气作用下,以雾化的形式从喷枪中向流化层喷入,使药物粉末聚结成颗粒。在整个制粒过程中,颗粒只受到流化床内部气流的作用,上下流动,因此形成的颗粒之间的粘合度较低,颗粒密度比较小,粒度比较均匀,并且有较好的可压缩性和流动性。流化床制粒设备的整体情况都大同小异,主要的不同在于雾化的粘合剂喷入的方式。按照喷嘴所在位置的不同,可以大体将流化床分为顶喷式、底喷式和流化床三类,这三类流化床的示意图如下图1-1所示。顶喷式流化床是将喷枪从腔体外部伸入到制粒室中,从流化层的上方自上而下进行喷液。颗粒通过气流的作用上升至喷嘴的位置,雾化的粘合剂从喷嘴喷出并将颗粒包裹起来,颗粒上升到一定的高度后回落,如此往复,顶喷式流化床一般用于制粒。底喷式流化床是喷枪中粘合剂的喷洒方向与进风气流的方向一致,侧喷式流化床的喷嘴安装在制粒室的内壁上,最明显的特点是在其底部安装有布风板,底喷式流化床和侧喷式流化床一般用于包衣。[align=center][font='times new roman']图[/font][font='times new roman']1-[/font][font='times new roman']1 [/font][font='times new roman']制粒[/font][font='times new roman']流化床[/font][font='times new roman']分类[/font][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]流化床制粒技术研究现状[/b][/size][/font]1959年,美国的Wurst首先提出了流化床技术,该技术以其工艺简单,操作时间短,劳动强度低等特点广泛应用于固体制药领域。我国于上世纪八十年代才引入流化床制粒设备,相对于国外来说起步较晚,因此对于流化床制粒技术的研究也相对较少。石海涛[font='calibri'][size=13px][3][/size][/font]等人使用流化床制粒技术解决了采用传统的湿法制粒批次间颗粒质量属性差异大,制粒终点难以把握的缺点,制出崩解性能良好的甲磺酸吉米沙星片。申楼[font='calibri'][size=13px][4][/size][/font]等人把颗粒的流动性、表面性状和崩解时限作为衡量颗粒质量的标准,采用正交试验的方法确定出流化床制粒的最佳工艺参数。东北大学的王正松[font='calibri'][size=13px][5][/size][/font]以颗粒的粒度为研究对象,建立并验证了流化床制粒最终颗粒粒度的机理模型,并且建立了预测颗粒粒度的回归模型。浙江大学的周家辉[font='calibri'][size=13px][6][/size][/font]针对流化床制粒室温度难以控制的问题,分析了流化床制粒温度影响因素,对流化床进行了热力学分析,并且设计了温度控制器。在国外近几年的研究中,Neugebauer[font='calibri'][size=13px][7][/size][/font]等人针对流化床分层制粒过程中颗粒形成干燥区的问题,提出了一种用于研究各种工艺参数对粒子动力学和工艺稳定性的影响的模型。Hayashi[font='calibri'][size=13px][8][/size][/font]等人对流化床造粒过程中颗粒生长和破碎的机理进行了研究,提出了一种基于离散元法和计算流体动力学相结合的粒子碰撞频率函数的粒子平衡模型。Heidari[font='calibri'][size=13px][9][/size][/font]等人考虑液滴蒸发过程引起的体积变化等因素,综合考虑粘合剂粘性与液滴表面张力的平衡力,建立了流化床制粒过程中液滴蒸发的力学模型,利用该模型研究了不同温度、蒸汽压力、接触角和液滴直径条件下蒸发速率对液滴扩散时间的影响。Teixeira[font='calibri'][size=13px][10][/size][/font]等人研究了提高姜黄素溶解度的多种策略并且以姜黄素为原料,采用流化床制粒法,制备姜黄素颗粒。国外的流化床技术已经取得了一定的成就,然而国内的流化床制粒领域中相关的文献报道却比较少,这种现状对于我们来说既是机遇也是挑战。通过文献可以看出,越来越多的学者都针对流化床制粒工艺进行研究,这也必将会是未来研究流化床制粒技术的一个趋势。
我们实验室属独楼,室外环境较差没有绿化,实验室为普通玻璃窗,配厚窗帘.实验楼东西走向南北朝向,仪器放置在楼道北侧背阴一边,现在仪器未使用任何遮蔽防护之类,开实验室门既是楼道,以前仪器使用的墨绿色号称绒布的,发现盖上之后有许多纤维掉在仪器上面,现在要为仪器重新制作防护罩,不知用什么的好?大家的呢?
[font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]流化[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]床[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]生产[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]工艺影响因素及研究现状[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b] [/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]流化[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]床生产[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]工艺影响因素概述[/b][/size][/font]流化床生产过程的内部机理比较复杂,很多因素都会影响制得颗粒的质量属性。其中,设备、工艺、处方等因素通常会对制粒结果有较大影响。设备因素主要是由于流化床本身造成的,不同的流化床制得的颗粒有所不同;工艺因素是与生产过程中实际操作的工艺参数相关;处方因素是指使用的原辅料性质和粘合剂的性质等有关。(一)设备因素在流化床制粒中,容器材料和形状影响比较大,容器的形状会对粒子的运动轨迹产生影响。流化床设备不但要使得物料可以达到流化状态,还要保证不会黏附在容器内壁上,这样可以使得在制粒过程中避免产生不规则的颗粒以及大量的细粉[font='times new roman'][size=16px][11][/size][/font]。流化床锅体的主要形状是圆锥体,上面比较宽,下面部分比较窄,其样式和内部结果如下图所示。[align=center][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][/align][align=center][font='times new roman'][size=16px]图[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]流化[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]床锅体图[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]图[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1-[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]流化[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]床锅体内[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]部图[/size][/font][/align]锅体一般是用低碳钢304作为材料,并且在锅体内部进行抛光处理。锅体的最底端是进风口,分流板就安装在进风口处,并且在分流板上固定一层不锈钢筛网。Borne等人提出,分流板不会对物料粉末粒子的运动产生影响。(二)工艺因素流化床的工艺因素主要有进风温度、进风量、雾化压力、粘合剂的流速等。流化床的进风温度要保持在合理的范围内,一般设定在25°C~55°C之间。如果进风温度过低,粘合剂不能够及时蒸发从而使得颗粒湿润过度,这样流化床内壁上就会黏附部分物料粉末,从而不能达到较好的流化状态,粒子容易粘成一团;如果进风温度过高,会使得颗粒上的粘合剂过早的被干燥,颗粒上附着的粘合剂变少,从而达不到良好的制粒效果。流化床的进风量也是一个很重要的影响因素之一,合适的风量可以使得物料能够处于很好的流化状态,对使粉末形成颗粒比较有利,提高进风量有利于大颗粒的形成[font='times new roman'][size=16px][13][/size][/font]。若进风量过大,细小颗粒中的粘合剂挥发过快,不能达到良好的粘合作用,使得颗粒的粒度分布比较宽,细粉相对来说也比较多;若进风量较小,颗粒不能够被很好的吹起来形成流化状态,在粘合剂的作用下容易形成粒径很大的颗粒,从而形成很大的一团,造成塌床。雾化压力可以影响喷雾雾滴的大小,雾化压力过低,形成的喷雾的雾滴变大,喷雾范围变小,造成粘合剂在物料中分布不均匀;雾化压力过高则喷雾的雾滴过小,不利于物料良好的流化状态,不能很好的制粒。粘合剂的流速跟流化床制粒室内的湿度有关系,粘合剂流速过高,颗粒不能够被及时干燥,容易有塌床的风险;流速过低时,喷入的粘合剂过少,则会使颗粒的粒径过小,粉末较多,导致制粒效率低下。(三)处方因素物料主要有疏水性和亲水性两种。疏水性物料一般采用干法制粒;亲水性物料由于亲水性的不同也会产生差异。亲水性越强的物料越不容易被粘合剂润湿,因此成粒难度较大,需要提高粘合剂喷入速度[font='times new roman'][size=16px][14][/size][/font]。粘合剂的种类和浓度也会影响粉末的成粒,是流化床制粒中比较重要的工艺[font='times new roman'][size=16px][15][/size][/font]。合适的粘合剂与物料之间具有较高的粘合力,有利于颗粒的形成。粘合剂浓度较高可以有较高的粘合力,制得的颗粒较大;浓度较低则会使得粘合力不够,导致制粒速度变慢,细粉增多。[font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]流化[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]床生产[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]工艺研究现状[/b][/size][/font]质量源于设计(Quality by Desigh, QbD)在药物制剂研究中常用的研究方法,通过对生产工艺的理解来对过程进行控制[font='times new roman'][size=16px][16][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][17][/size][/font]。在流化床制粒过程中,如果采用不同的工艺参数,则制备出来的颗粒的尺寸、粒径分布、含水量、流动性、可压性和溶解特性等质量属性都会有所不同,从而影响制成的颗粒的最终品质[font='times new roman'][size=16px][18][/size][/font]。已经有不少国内外学者在流化床制粒工艺方面进行了研究。宋顺宗[font='times new roman'][size=16px][19][/size][/font]等人采用正交试验的方法研究了进风温度、雾化压力和包衣液流速等工艺参数对包衣颗粒完整度、效率和成品率的综合影响。余楚钦[font='times new roman'][size=16px][20][/size][/font]等人以进风温度、进风参数、粘合剂流量、雾化压力为自变量采用正交试验的方法,考察这些工艺参数对颗粒的粒度、流动性、表面性状及崩解时限的影响。比利时布鲁塞尔自由大学的Rambali [font='times new roman'][size=16px][21][/size][/font]等人研究制粒过程的进风温度、进风速度、喷雾速率和进风湿度等工艺参数,确定了颗粒的理论含水率和液滴尺寸的测量方法,并且用这些工艺参数作为变量,建立了与粒径尺寸的回归模型。Aleksić [font='times new roman'][size=16px][22][/size][/font]等人采用响应面分析、多层感知机神经网络和偏最小二乘法对流化床制粒过程进行了数值模型来设计工艺参数的调节范围,研究表明,粘合剂的粘度会在很大程度上影响颗粒的形状。Bellocq[font='times new roman'][size=16px][23][/size][/font]等人研究了流化床制粒在不同工艺条件下对团聚体结构和功能的影响。Ehlersa[font='times new roman'][size=16px][24][/size][/font]等人在粘合剂流速、流量和进风温度恒定的条件下,研究脉冲喷雾和雾化压力在顶喷式流化床中对颗粒粒径大小的影响,结果表明,雾化压力对粒径的影响取决于入口空气的相对湿度,脉冲喷雾的占空比对最终产品的质量至关重要。目前为止,流化床制粒工艺主要依靠工人的经验,具有较强的主观性,缺乏对工艺参数和质量属性之间的深入理解,很少考虑制粒过程中质量属性的变化,缺乏有效的实时监控手段,同时还有很多的不确定性因素。因此,实施过程监控手段,实时测量流化床制粒过程中的关键质量属性对理解工艺参数对颗粒质量属性的影响具有重要作用。
请问有哪位大哥知道,工厂用的振荡流化床的具体使用操作规程吗??发个给我,谢谢我这里用的振荡流化床型号:ZLG6*0.6邮箱:lwj2380@126.com [email]luwj@fenchem[/email].com
循环流化床锅炉(CFB)具有高效、低污染、煤种适应性广、负荷调节性好、不易灭火、灰渣可利用等特点,采用洁净燃烧技术,符合国家环保产业政策,再加上其较好的煤种适应性,在我国得到迅速推广,配套机组在向300MW及以上方向发展。 循环流化床锅炉由于其结构的特殊性,所安装的热工仪表测量、保护仪表与常规煤粉炉相比,有许多类似之处也有明显的区别。CFB锅炉汽水系统的测点及其作用与普通煤粉炉相同,烟风系统增加了一些为CFB锅炉专设的风机风道的压力、温度和流量的测点,其测量方法也同普通煤粉锅炉相同。CFB锅炉在参数测量方面的特别之处在于对炉膛、分离器、回料阀和冷渣器等固体流道参数的检测。 一、循环流化床锅炉的运行特点 CFB锅炉在运行过程中特别要注重对床温、分离器入口温度、风煤比以及床压的监测、调节及控制,注重对影响物料流化、循环及燃烧的各种风量的监控,确保建立一个平稳、足够的热物料循环,从而完成锅炉燃烧的燃料燃烧及热量传递过程。 按照循环流化床锅炉的特点,设置炉膛温度、床温、床料高度及其它有关测量仪表测点,以保证机组的安全、经济运行。压力测点应提供接口和防堵设施,温度测点要求留有热电偶插座,对有防磨要求的温度测点应加装防磨装置。 二、主要热工参数的作用和意义 2.1床温 床温是CFB锅炉的重要运行参数。所谓床温主要是指燃烧密相区内流化物料的料层温度,床温值是由锅炉结构、灰熔点、排放物指标(因煤种不同而有所区别)等综合因素决定的,通过调节流经布风板的一次风量和直接进入炉膛的二次风量之比来维持床温,同时注意控制给煤量,保证温度在850-925℃,使其处于最佳燃烧状态,并有利于炉内石灰石脱硫。床温过高或过低将造成锅炉结焦灭火。影响床温的因素主要有煤种、给煤量、一/二次风量、返料量及冷灰循环。在循环倍率一定时,主要与煤量和风量有关,其中一次风量起主要作用。 以一台480t/h容量的东锅锅炉为例,它设置了2层床温测点,下层24个测点,上层24个测点,左右侧分为四列三排。它们均在二次风口以下,密相区之内,每层测点沿炉膛前中后三排均匀、对称布置,每层测点的输出送入平均值计算回路,以计算床温平均值。同时各测点均进入DCS显示。当有点与平均温度相差150度时,判断此为坏点。 2.2床压 床压是料层高度的反映。运行中通常通过调整排渣量的多少控制床压的高低。床料多、床压高,对于稳定燃烧、减小短时间断煤波动的影响、减少排渣可燃物含量有利;但同时床压高会增大一次风压头,电耗增加,同时也大大增加了启动点火阶段加热床料的时间,降低运行经济性。床料薄、床压低,易造成布风不均匀,引起结焦。 床压一般是指密相区的床压,床压测孔一般布置在距布风板上端面250mm处,左侧3个,右侧3个,将3个压力测量值通过3取中逻辑判断后送至显示及报警回路;3者取平均值作为床压调节系统的反馈信号。控制床压的方法,通过控制排渣系统来维持炉膛床压恒定,也即确保炉内的灰平衡和床料构成。 2.3风量 循环流化床锅炉的运行基于流态化的高温物料悬浮燃烧。燃烧风量是运行人员调整燃烧的的重要依据,其测量的准确性直接影响到锅炉的经济安全运行。在机组安装完成后,调试运行前,应当对一、二次风机性能进行测定,并对风量的标定,主要是鉴定风机的出口风量、风压能否达到设计要求,能否满足燃烧需要,并且校正测量装置的准确性。有效的测量风量,有利于一二次风比例的调整,能改善炉内风、煤、灰的混合程度,达到最佳的燃料、供风混合方式。 2.4点火风道温度 由于CFB锅炉的炉膛密相区和旋风分离器等多个部位设有较厚的耐磨耐火材料,因此,在启动过程中必须严格控制加热升温速度,以防止这些非金属材料因受热不均而爆裂脱落。这就要求CFB锅炉的启动燃烧器设计既要位置合理又要有较宽的调节比,而且操作灵活,可控性高。 CFB锅炉的启动燃烧器一般有3类,即布置在布风板上的床上启动燃烧器、床枪和布置在布风板下的热烟发生器。东锅早期设计的流化床采用床上加床下点火器,但后来的产品仅仅保存了床下燃烧器,床下燃烧器的风温是个重要的监测参数。 在DG490/13.8-II2型锅炉,设计有风室温度和点火风道温度各二支,分为左右侧。在点火时,通过调整燃烧将床下油点火器出口烟气温度控制在980℃以下,且风室温度在870℃以下,在此期间,温升率建议不超过28/每20~30分钟。 三、运行情况与改进措施 由于CFB锅炉内进行固体燃料的循环燃烧,流动的物料极容易堵塞压力测点和测压管线,同时对测温元件产生强烈的磨蚀,用常规手段难以进行准确可靠的连续测量,床温和床压测量元件均采用耐热防磨及防堵措施使所测数据准确、可靠。而床温、床压等参数对保证CFB锅炉的安全经济运行至关重要,因此必须采用特殊的防堵、防磨测量手段。 3.1床温测量的改进 东锅的循环流化床炉膛床温元件通常是采用多点铠装热电偶,在布风板的前、中、后三个位置横向各安装8套铠装热电偶,每套热电偶由伸出布风板的距离为300mm,由耐磨保护套管保护;每套热电偶有双只铠装热电偶组成,一点测上床温,一点测下床温。热电偶安装方式为由前后墙平插入风室,经90°直角向上穿过并固定在布风板上的耐磨保护套管内。中间的测温元件从前墙插入。在机组启动调试期间,由于温度元件在风室内的部分太长,在一次风力作用下晃动太大,首批安装的24套热电偶全部损坏。经分析:床温元件在风室内的部分太长且不能很好固定,床温元件容易被风室内的高温风冲刷,造成损坏。后虽经过采取增加不锈钢保护套管、用耐磨浇筑料及钢丝网包裹、用耐火砖固定等方法进行处理,使床温元件的工作条件有所改善,但仍然没有从根本上解决问题。 因此,在大修期间我们建议对床温元件进行改造,安装方式均为炉底直插向上穿过布风板方式,同时加装耐磨保护套管,在套管外侧再增加耐磨浇筑料。如图所示,这种方式不但能有效保护测温元件,而且能够实现温度元件的在线更换。 3.2床压测量的改进 在国内440t的流化床锅炉在运行过程中,床层差压,床层密度,床层压力等几个测点经常结焦。在最初的安装中,测点取样与炉壁成45度向上,加装风烟自动分离器。但是使用时间较长后,依然会堵塞。后经改进后,采用自动吹扫装置,向测孔引入一股恒压吹扫空气,通过调节取样管与吹扫管的距离,实现自动补偿,解决了既要取压防堵又要测量准确的问题。如图所示,通过前后调节吹扫管在取样装置锥口的位置,实现自动吹扫补偿。 在吹扫口的吹扫气源上,特别且加装了调压稳压器,完全解决了电厂气源不稳的问题,确保了流量控制器的正常运行。 3.3点火风道温度的改进 在运行过程中,点火风道温度元件插入深度过长,被高温风吹刷,以致于保护管和热电偶同时损坏。经检查,热电偶保护管已穿过浇筑料80MM,测量的已不是壁温,而是烟温。后将热电偶保护管调整,露出浇筑料10-20MM,同时在测量元件对侧又加装一个测温点,构成A、B二点,即保证测量的灵敏度,又提高元件应用的可靠性,有利用缩短启动时间,为经济运行提供基础。 3.4风量测量元件的改进 风量对于流化床锅炉来说,无疑是一个重要参数,无论是设计还是调试、运行人员,都希望表计的读数能真实的反应实际的工状。一、二次风机性能的测定和风量的标定,主要是鉴定风机的出口风量、风压能否达到设计要求,能否满足燃烧需要,并且校正测量装置的准确性。在测量中应注意,虽然一般都采用标准的测风装置进行风量测量(目前最普遍的是采用机翼型测风装置)。 但是在实际施工中,设计的安装在锅炉风道上的风量测量装置,往往由于锅炉风道截面大,直管段长度短,弯头多,按厂家要求管道直段不能满足测量,在加上装置加工误差等原因使流量系数偏离设计值,因此必须对其进行标定。由于流量与风温、差压、风压的关系较大,有的采用了三种取样元件分别测量其参数,造成测量装置折线系数公式相当繁琐,其故障自检能力也基本没有。因此当然,有必要采用先进的测量元件器可以减少测量误差。 在实际应有中,我们选用了热式质量流量计,经过一年多的运行,相比于其它测量风量的元件相比,具有性能优良、可靠性高的特点。该产品基于热扩散技术,其典型传感元件包括两个热电阻,当这两个热电阻被置于流体中时,其中一个被加热,另一个用于感应过程温度。两个热电阻之间的温差与过程流速及过程介质的性质有关,保持该温差恒定,则电子单元加热热电阻的能量与质量流量成一定的比例,我们就能推算出风量。 3.5给煤系统的改进 在锅炉试运过程中出现最频繁的问题是煤仓堵煤,为保证正常运行,在煤仓开设人工捅煤孔,有一次断煤时,就地观察员工打开捅煤孔捅煤,破坏了给煤机的压力平衡,炉内烟气反窜到给煤机,造成一台给煤机皮带及其它部件烧损。给煤机厂家对此进行了改造,在给煤机进煤口安装了测温元件,信号送入DCS作为是否超温的判断条件,同时联锁快关阀。当炉内有热烟气反窜到给煤机时,通过温度信号使快关阀迅速关闭。原来的电接点双金属温度计作为给煤机就地控制柜的报警信号。 通过调试,对电厂运行人员建议:六台给煤机尽量采用对称投运和两侧炉膛给煤量比
[align=center][size=21px][b]流化床[/b][/size][size=21px][b]混合环节[/b][/size][size=21px][b]及与[/b][/size][size=21px][b]PAT[/b][/size][size=21px][b]技术的集成[/b][/size][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px]流化床[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]fluidized bed[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]),指首先[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]利用气[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]流动使[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]物料呈[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]沸腾状态,再喷入雾化后的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]粘合剂进行后续的制粒、包衣、成丸等,最后得到干燥的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]颗粒、微丸、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]包衣粉末及包衣微丸[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的制药设备。在流化床制药[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]过程中,物料的混合、制粒[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]、[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]包衣[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]干燥[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]等[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]同时完成。流化床技术是在上世纪五十年代发展起来的,最初设计只是用作干燥设备,以提高干燥效率。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1964[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]年[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Scott[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]等将[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Wurster[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]方法作了改进并应用于医药工业,我国于上世纪八十年代将流化床引入到口服固体制剂的制备过[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][color=#080000][1][/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]与传统制药工艺相比,流化床工艺设备具有以[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]下优[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]点[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][color=#080000][2, 3][/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]:([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])将固体制剂制备过程中多个生产环节有机结合在一起,生产工艺高效、便捷且提高了自动化程度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]缩短了工艺周期;([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])所得制剂产品有更好的流动性、同质性、可压性;([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])生产在密闭环境中进行,无交叉污染;([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])为湿热敏感药物的制备提供了良好的解决方案。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]随着制药机械设备的发展,流化床设备发展趋势如下:([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])规格越来越齐全,批次处理能力从几升到几千升;([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])集成智能传感器,达到对[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]生产工艺的全自动化[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]监测[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]控制[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px];([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])物料无交叉连续化传递,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]整个生产过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]全密闭、无尘化操作[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px];([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]4[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])工艺灵活,通过与其他设备集成形成连续化生产。[/size][/font][align=center][img='']" alt="[/img][/align][align=center][font='times new roman']图[/font][font='times new roman']1-1[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']流化床与其他设备结合形成制粒流水线[/font][/align][align=left][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]流化床混合[/b][/size][/font][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px]流化床制药[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]工艺凭借其无可复制的优点[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][color=#080000][4, 5][/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]固体制[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]剂生产过程中得到了广[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]泛的应用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][color=#080000][6, 7][/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。然而,流化床制药生产过程是一个密闭的过程,物料的流化状态剧烈且不可见,很难获取腔室中物料的状态和理化性质。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]PAT[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]技术的集成[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]随着制药设备的发展,流化床设备与其他制药机械设备结合形成固体制剂连续化生产系统[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],如[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]图[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1-1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。作为固体制剂生产的上游关键环节,混合过程物料的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]混合[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]均匀度会影响到制药过程下游每个环节[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量的均匀度,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]这[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]也是药品质量一致性评价的重点。因此,流化床混合过程粉末共混物中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的瞬态干扰检测是一个重要[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]研究课题。但目前国内流化床混合过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]CQAs[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]测定多采用离线方法,只有在混合过程的最后,分析人员才能检测产品的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]CQAs[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],以决定产品是否达到放行标准。此外,离线分析具有破坏性、昂贵、费时费力的缺点,不能及时反映生产过程物料的真实状态,最终影响产品的质量和安全性。因此,对流化床混合过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]进行实时监测研究,能够加深对产品和工艺的理解及后续生产过程的控制,实现精益生产与偏差控制的结合。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]仿制药一致性评价的推行对制药行业提出了更高的要求。固体制剂是目前最重要的给药形式之一,作为固体制剂生产的上游关键环节,混合过程物料的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]均匀度会影响到制药过程下游每个环节[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的含量均匀度,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]也是药品质量一致性评价的重点[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]只有实时在线监测产品的质量属性、过程中材料和工艺条件的变化,进一步对药品生产过程加以监测和控制,才能生产出符合要求的产品。但是目前通常采用的检测方法为离线取样检测,不能及时了解过程中物料的状态及理化信息。为此,探索并建立一套及时准确的流化床混合过程智能分析技术非常必要。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]过程分析技术的提出,为实现过程理解提供了技术及设备支持。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NIRS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]作为重要的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]PAT[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]工具,在混合过程中的应用稳步增加。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]将[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NIRS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]引入到流化床混合过程中,对混合过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量进行实时监测,加深对产品和工艺的理解及后续生产过程的控制,实现[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]精益生产与偏差控制的结合。同时,获得了[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]完整的关键质量参数数据,使产品质量有据可依、有据可查。因此,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]通过对流化床混合过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NIRS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]过程分析研究,建立混合过程智能控制关键技术,这将为整个固体制剂药物生产过程质量管理提供借鉴和技术手段。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]流化床[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]混合过程中,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]腔室内粉末共混物[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的瞬态干扰检测是一个重要的研究课题。然而,在实际生产中流化床混合过程具有[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]不[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]可见性,流化床腔室中物料的化学和物理性质的真实状态无从知晓。所以使用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]PAT[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]技术监测混[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]合过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量均匀性的价值不言而喻。为了实现流化床混合过程的可视化,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]在实验模拟型流化床上将过程分析技术[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NIRS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]引入到流化床混合过程中,对过程关键质量属性[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]—API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量进行[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]定量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]监测。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]目前,批次混合过程中的一种常见建模方法是使用多个批次的样本建立校准模型,但在生产条件下要收集具有代表性的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]校准[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]集需要[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]消耗大量的物料,否则会影响后续模型的稳健性。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]在小试实验型流化床中使用有限的原辅料建立校准光谱模型,用于监测流化床混合过程中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]加之[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]研究了光谱预处理和波段选择方法,建立[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]PLS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]模型来[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]预测[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量。在有效的光谱预处理和波段选择方法的帮助下,近红外传感器可以准确地测定混合物中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的含量,从光谱监测的角度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]NIRS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]用于流化床混合过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量均匀性检测的可行性。同时,增加了对工艺过程的了解,从而科学有效地控制生产过程,提高产品质量,保证产品安全。[/size][/font]
寻求流化床造粒,实验室用,要求与样品接触部分是有机类材料,不能有不锈钢含铁类物质。拜托各位,发布内容有效日期17年12月5日-17年12月30日
那位高手能设计或制作小型实验室用秸秆流化床 要求: 物料尺寸:2-4mm 能同时用两种气化气氛 外部电加热 有兴趣的请联系:15940443185
XRF, X射线荧光光谱仪,在有害物质检测,金属成分分析,膜厚测试等领域中有着广泛的使用。相对于其他精密检测仪器,XRF有着价格低,分析元素多,操作维护简易等优势,因而在大中小企业中,都有着不错的应用。电子行业中,XRF是最常见的RoHS有害物质检测仪器,但对于辐射防护,很多中小企业并不了解,这里,专门针对辐射防护,进行下简单的阐述。首先,与辐射有关的法规还是挺多的:《X射线衍射仪和荧光分析仪卫生防护标准》,《放射性同位素与射线装置安全和防护条例》,《电离辐射防护与辐射源安全基本标准GB 18871-2002》《放射工作人员职业健康管理办法》……我摘选些与我们密切相关的内容进行归纳。根据射线装置对人体健康和环境可能造成危害的程度,从高到低将射线装置分为I类, II类, III类(危害程度由高到底),按照使用用途分为医用射线装置和非医用射线装置。工厂中常见的XRF放射源多为3类,少量2类。按《放射性同位素与射线装置安全和防护管理办法》要求,所有生产、销售、使用放射性同位素与射线装置的单位都需做好场所及人员的安全与防护等,规范的工厂XRF使用端基本要求包含:1,办理辐射安全许可证(装置辐射豁免可不用) 2,必要的标示及中文警示说明 3,相关人员参加辐射培训(初级)(辐射培训单位需要有必要的资质,且取得培训证书的人员需每四年再训一次。)4,对辐射工作人员进行个人剂量监测(人员佩戴个人剂量计),并建立工作人员个人剂量档案,监测结果异常时应立刻核查并报告。《X射线衍射仪和荧光分析仪卫生防护标准》有更多仪器本身的防护要求,包含:1,不同位置的射线的空气比释动能率要求(详细要求见附件)2,X射线管防护套窗口的过滤片应符合ZB Y 226所规定的要求,3,过载保护:4,联锁装置“专用锁一总电源”联锁和“防护罩一高压”或“防护罩一遮光器”联锁 5 ,警示和标志 6,剂量监测等。此外强调下,剂量监测除个人剂量监测的,还包含场所剂量监测——有下列情况之一时应当进行场所剂量监测:a) 变更分析仪原配套的受照射部件或变更其装配结构、装配位置;b) 校准、调整分析仪的有用线束;c) 分析仪的屏蔽防护设备变更或损坏;d)超过规定的检测周期。《放射工作人员职业健康管理办法》中,更强调的是职业健康安全方面:除了前面法规有提到的个人监测和辐射培训外,从业资格判定及体检也是重中之重:未进行职业体检或岗前体检不合格,未成年人,怀孕及哺乳期妇女都是不得从事放射性工作的。体检上,当然都是指针对辐射从业人员的特殊岗位体检,项目是要比普通体检多很多。上岗前的岗前体检,在岗时每年都要进行的岗中体检,离职前的离岗体检,以及出现监测异常时的应急事故体检,以上四项检查项目略有区别(祥见附件)。另外,办法还提到,进入辐照装置、工业探伤、放射治疗等强辐射工作场所时,除佩戴常规个人剂量计外,还应当携带报警式剂量计。工厂内XRF一般辐量射较小,不强制要求,但若能配备一个,会更好。规范的大公司,可以完善做到辐射防护:办理辐射许可证,人员的完善体检,规范的标示,个人剂量计,报警式剂量计,人员辐射培训,辐射档案记录,环境辐射监测,防辐射服配备等。而很多小公司,无法按要求做到规范,出于人员安全考虑,辐射体检和辐射剂量应该为最基本的防护要求必需做到,在条件许可的情况下,应逐步完善。
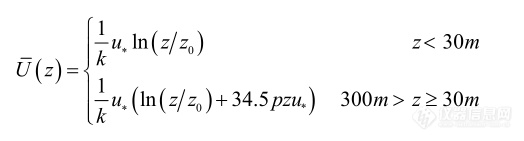
[align=center][size=16px][b]流化床风荷载模拟[/b][/size][size=16px][b]在[/b][/size][size=16px][b]matlab[/b][/size][size=16px][b]中的实现[/b][/size][/align]风是由空气流动形成的,结构处于风场中会受到顺风向力、横风向力及扭风力矩,对于流化床结构主要考虑顺风向风荷载及其作用效应,其风速时程曲线中主要包括长、短周期两种成分,因此可将顺风向风荷载分解为平均风(即稳定风)和脉动风(也称阵脉动风)两种成分。其中,由于风的长周期成分频率一般远小于结构的自振频率即频率比接近于零,所以结构的动力放大系数接近于一,这部分风荷载产生的结构动力效应很小,可以忽略,因此一般等效为静力作用,此部分风荷载的作用效果是使结构产生平均侧移;而脉动风是由湍流引起的,其变化具有随机性,且脉动风周期较短,其中会有一部分与结构的自振周期较为接近,此时结构的动力放大系数较大,产生了不可忽略的动力响应,脉动风部分将使得结构在平均侧移附近摇晃。由上述分析可见风荷载的模拟重点为两个方面,即平均风成分和脉动风成分的模拟。本文根据实验室流化床的设计资料及结构特点,使用 Matlab编制程序,通过基于自回归(Auto-Regressive,AR)模型的线性滤波法模拟了结构所受的风荷载时程,并验证了模拟风荷载的可靠性。与频域分析方法相比,时域分析方法更适用于流化床体系这种结构的分析(结构必然已经进入非线性阶段)。因此,在进行分析之前,首先要正确模拟结构所受到的风荷载时程。目前结构模拟风速时程的常用方法为谐波叠加法、线性滤波法 ,以及小波分析、逆傅立叶变换等,其中,最常用的方法即为谐波叠加法和线性滤波法。与谐波叠加法相比,线性滤波法的突出特点是计算量少,效率高,在脉动风风速的模拟中得到了广泛的应用 。针对这种情况,利用基于数字滤波技术AR 模型的线性滤波法来模拟其风荷载时程。如前文所述,风荷载可分为平均风成分和脉动风成分,因此接下来的风荷载模拟也主要分为这两个部分。根据实测结果,目前平均风速沿高度的变化关系(又称为风剖面)常用指数函数和对数函数来描述。本文采用对数风剖面建立平均风场,选取 ESDU建立的修正对数风剖面,其表达式如下式所示:[img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031744568784_7101_3890113_3.png[/img]式中, z 为任意一点的高度 ;z0 为地面粗糙长度; k 为 Karman 常数;u 是摩阻风速; p 是 Coriolis 参数,取 p =10 -4 s -1 。视脉动风速时程为平稳高斯随机过程,本文顺风向风速谱按照紊流尺度随高度变化 Kaimal 风速功率谱进行模拟,其谱密度函数如下:[img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031744570398_6514_3890113_3.png[/img][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031744581558_6648_3890113_3.png[/img][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031744591830_7644_3890113_3.png[/img][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031745000308_6331_3890113_3.png[/img]其中, S 为输电塔的体形系数取值为 2.3; A 为结构沿风速方向的构件投影面积之和。 通过以上算法及公式成功的实现了使用matlab对流化床中风荷载进行模拟探究。
x射线衍射仪和荧光分析仪卫生防护标准Radiological standards for X-ray diffraction and fluorescence analysis equipmentGBZ115-20021 范围 本标准规定了X射线衍射仪和X射线荧光分析仪的放射防护标准和放射防护安全操作要求。 本标准适用于X射线衍射仪和X射线荧光分析仪的生产和使用。2 规范性引用文件 下列标准中的条款通过本标准的引用而成为本标准的条款。凡是注日期的引用文件,其随后所有的修改单(不包括勘误的内容)或修订版本均不适用于本标准,然而,鼓励根据本标准达成协议的各方研究是否可使用这些文件的最新版本。凡不注日期的引用文件,其最新版本适用于本标准。 GB4075 密封放射源分级 GB4076 密封放射源一般规定 GB8703 辐射防护规定 ZBY226 X射线衍射仪技术条件3 术语和定义 下列术语和定义适用于本标准。3.1 X射线衍射仪和X射线荧光分析仪 X-ray diffraction equipment and X-ray fluorescence analysis equipment X射线衍射仪 利用X射线轰击样品,测量所产生的衍射X射线强度的空间分布,以确定样品的微观结构的仪器。 X射线荧光分析仪 利用射线轰击样品,测量所产生的特征X射线,以确定样品中元素的种类与含量的仪器。 以下把X射线衍射仪和X射线荧光分析仪统称为分析仪。3.2 闭束型分析仪和敞束型分析仪 enclosed-beam analytic analytical equipment and open-beam analytical equipment 闭束型分析仪 以结构上能防止人体的任何部分进入有用线束区域为特征的分析仪。 敞束型分析仪 结构上不完全符合闭束型分析仪特征的分析仪,操作人员的某部分身体有可能意外地进大有用线束区域。3.3 射线源 radiation source 本标准中,射线源特指X射线管或能便样品受激后发出特征X射线的密封型放射性核素源(以下简称密封型源)。3.4 联锁装置 interlocking device 分析仪的一种安全控制装置,当其中相关的组件动作时可以发出警告信号,或能够阻止分析仪进入使用状态,或使正在工作的分析仪立即关停。3.5 有用线束 primary radiation 来自射线源并通过窗、光栏或准直器射出的待用射线束。3.6 受照射部件 exposed components 分析仪中受到有用线束照射的部件,如:源套、遮光器、准直器、连接器、样品架、测角仪、探测器等。3.7 源套 radiation source housing 套在射线源外部的具有一定防护效能的壳体,分为密封源套和X射线管套。3.8 防护罩 protective enclosure 敞束型分析仪中,用来屏蔽源套和所有受照射部件的一种防护设备。在防护罩的侧面,通常装有可以平移的防护窗,调试、校准等操作结束后,关闭防护窗,能够有效地防止人员受到有用线束和较强散射线的照射。3.9 遮光器 shutter 安装在有用线束出口处的可以屏蔽有用线束的器件。
准备购买流化床干燥机,那位厂家能介绍一下产品性能。
[align=center][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]分析技术应用于流化床[color=#1d1b11]制粒和包衣[/color]过程的研究进展[/align][b][/b][align=left][b]摘要[/b][/align][align=left]目前流化床制粒、包衣技术在我国制药行业中因其具有制得颗粒流动性、压缩成型性好,微丸包衣厚度均匀等诸多优点而受到广泛应用。随着过程分析技术的推广,针对于关键质量属性的在线分析受到越来越多的关注,以采用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]分析技术为代表的过程分析技术可以对流化床制粒、包衣过程进行有效地监测,从而提高产品质量、保证产品安全性。本文针对流化床制粒、包衣过程中水分含量、粒径大小、包衣厚度等关键质量属性,综述了[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]分析技术在监测流化床制粒、包衣过程的研究进展,表明[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]分析技术可以有效的监测流化床生产过程各关键质量属性。通过综述旨在为我国制药行业的流化床制粒、包衣单元实现自动化控制和智能生产提供参考。[/align][align=left] [/align][align=left][b]关键词:[/b][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]技术;流化床制粒;流化床包衣;过程分析技术;在线监测[/align][b]Abstract[/b][align=left]Thetechnologys of fluidized bed granulation and pellets coating are widely used inpharmaceutical industry. Particles made in a fluidized bed have good liquidity,compressibility, and coating thickness of pellets are homogeneous. Near-infraredspectroscopy can real time monitor in fluidbed granulation and coating process, so it can improve the productquality and ensure product security. This review gives research progress of Near-infraredspectroscopy monitoring in fluid bed granulationand coating process, and gives quantitative analysis model of moisture content, particle size and tablet/pelletthickness to realize in-line monitoring and controling.[/align][b][color=black]Key words[/color]:[/b][color=black]Near infraredspectroscopy [/color]Fluidized bed granulation Fluidized bed coating Process analytical technology In-line monitoring[align=left][b]前言[/b][/align]流化床又称沸腾床,其过程为通过气流将物料呈流态化,再喷入雾状液体对物料进行制粒或包衣。该方法可以集混合、制粒、干燥或包衣于一体,与湿法制粒、熔融制粒、包衣锅滚制等传统方法相比具有以下优点[sup][/sup]:工艺简单,生产效率高;在密闭的环境中生产,防止外界环境对物料的污染;制得的颗粒流动性好,粒度均匀、压缩成型性好;包衣厚度均匀,干燥效率高。近年来流化床技术在我国医药行业已得到广泛应用,但目前国内流化床技术(干燥、制粒、包衣)同样存在许多问题,产品关键参数的测定多依靠经验,传统的离线测定方法具有破坏性、昂贵、费时费力,且离线分析会使得参数的检测滞后于生产,检测结果难以反映生产过程的真实状态,因此产品多出现稳定性、均一性较差的问题,影响了最终产品的质量和安全性。目前一致性评价和连续化生产等对参数的在线优化提出了更高的要求。[align=left]美国FDA于2004年以工业指南的方式颁布了Processanalytical technology(PAT),旨在通过过程分析技术(PAT)提高对药品研发、生产和质量全过程更加科学性的控制[sup][/sup]。为保证产品的安全、有效、稳定、均一,近年来,研究出现多种用于流化床制粒和包衣过程的PAT在线分析仪器,以实现对生产过程的在线监控。[color=black]例如,[/color][color=black]3D[/color][color=black]图像分析技术([/color]3D imaging method)用于流化床制粒过程,在线测定颗粒粒径大小[sup][/sup];在流化床微丸包衣过程中,Mož ina等[sup][/sup]研究了数字成像技术(digital imaging)在线监测微丸包衣厚度以及判断微丸粘连问题的可行性。但应用图像分析技术需把颗粒或微丸当作理想的球体计算,难以准确测量颗粒粒径和包衣厚度。此外,聚焦束反射法(focusedbeam reflectance method,FBRM[color=#231f20])作为一种[/color]PAT工具用于监测因粘合剂溶液过量而产生的颗粒凝聚问题以及用于测定粒径大小[sup][/sup];[color=#231f20]Sheahan[/color][color=#231f20]等应用声波发射([/color]acoustic emissions[color=#231f20],[/color]AE)监测流化床顶喷包衣喷嘴的堵塞问题,且进行了用于监测包衣厚度的研究[sup][/sup]。[color=#231f20]FBRM[/color][color=#231f20]广泛应用于结晶过程,而应用在流化床制粒过程中,目前没有相关文件支持[/color][sup][/sup][color=#231f20];声波发射技术监测包衣厚度的可行性还需更深入的研究。为了克服以上分析方法的弊端,我们需要一种更实用的在线分析技术。[/color][color=#231f20]此外,[/color]Tok等[color=#131413][/color][color=#131413]研究了[/color]FBRM[color=#131413]、[/color]AE以及[color=#131413][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S[/color][color=#131413]三种[/color]PAT技术应用于流化床制粒过程在线监测的可行性,在制粒生产过程中,其中AE技术易于受制粒过程中空气流速以及外界因素的影响;FBRM和[color=#131413][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S[/color][color=#131413]的光纤探头易被样品污染,影响在线数据的采集。但许多研究表明[/color][color=#131413],可以通过安装吹扫装置保持[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S探头的清洁。[/align][align=left]目前[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]技术(Near-infraredspectroscopy,[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S)作为PAT的有力工具,其波长范围为700-2500nm(14286-4000cm[sup]-1[/sup])之间,主要反映含氢基团(如C-H,O-H,N-H、S-H等)振动的倍频和合频吸收[sup][/sup]。[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S分析样品含量大于千分之一,这符合一般生产要求,且其以分析速度快、非破坏性、无污染、投资少、操作技术要求低等特点在制药行业的应用日趋广泛。本文综述了在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S在流化床干燥、制粒和包衣过程中应用,旨在为我国制药行业的流化床制粒、包衣单元实现自动化控制和智能生产提供参考。[/align][b]1 [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]应用于流化床制粒干燥过程[/b][align=left]随着计算机技术、光纤和化学计量学的发展,在制药行业质量要求日趋严格的大环境下,发展以[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S为主的在线监测研究势在必行。[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S在线监测流化床制粒干燥过程,连续采集过程中的光谱,可以对过程中颗粒的水分含量、粒径分布以及堆密度等关键参数进行监测[sup][/sup],从而对整个制粒干燥生产过程进行过程控制。[/align][align=left][b]1.1 颗粒的水分含量[/b][/align][align=left]在流化床制粒干燥过程中,颗粒的含水量可影响颗粒的流动性、可压性以及药物的稳定性。且含水量对制粒过程也会产生影响[sup][/sup],若在制粒过程缺少监测控制,易造成物料含水量过高或过低;含水量过高,易结成团块,造成塌床;含水量过低,颗粒的粒径小,会造成颗粒中粉末较多,由此可见,对流化床制粒过程进行过程控制[color=black]是非常重要的。水的[/color]O-H[color=black]伸缩振动一级倍频在[/color]1440 nm[color=black]附近,较强的合频吸收谱带在[/color]1940nm[color=black]附近,在早期,[/color]Rantanen[color=black]等[/color][sup][/sup] [color=black]采用[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S[color=black]对流化床制粒过程中颗粒的含水量进行监测研究,表明测定过程使用与水分相关的波长而去除无关波长信息,可以更准确、更迅速地监测制粒过程中含水量的变化。[/color][/align][align=left][color=black]而且,除了进行水分定量分析监测流化床制粒干燥过程外[/color],还可利用主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA[color=black])对过程中的多维变量进行降维分析,实现数据的可视化。此外,[/color]Rantanen等还研究了在流化床制粒过程中,利用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S水分测定,结合过程中温度和湿度的测定对制粒过程的含水量进行监测,以实现制粒过程的控制与监测。以上研究中,是[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S漫反射光纤探头透过流化床制粒机上的视镜来监测制粒过程中含水量的变化。[/align][align=left]除此之外,还可将光纤探头安装到流化床内部进行接触式在线采样。Kona等[color=black]在实验室规模流化床制粒机([/color]1-L)中安装一特制的勺状探头,并在探头上端位置安装压力吹扫装置,待光谱采集完毕后,启动吹扫装置,样品返回流化床[color=#231f20]内继续参加制粒,[/color]并在探头[color=red]等同的[/color]位置收集样品进行一级数据的测定。[color=#231f20]结合偏最小二乘[/color](partial least squares,PLS)算法对流化床制粒过程中样品的含水量进行在线监测,并且结合多维主成分分析(multi-way principal component analysis, MPCA)建立多元统计分析控制方法,对异常批次进行判断。同时研究中对制粒过程中的进风温度和湿度、产品的温度和湿度进行在线监测,通过对生产过程中产品的含水量、温度和湿度的监测以实现实时错误诊断和过程控制。与此类似,Peinado等[sup][/sup][color=#231f20]将[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S光纤探头嵌入到流化床中进行光谱采集,通过监测含水量的变化对生产规模流化床(300-L)干燥终点进行判断。研究中采用标准正态变量变换(Standard normal variate , SNV)预处理方法消除表面散射对[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]漫反射光谱的影响,1940nm附近有较强的O-H合频吸收谱带,由此,采用1854-2075 nm波长建立了PLS水分定量模型。为了证明模型的适用性,用外部验证集对模型进行独立验证,并对[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S方法进行方法学验证。与前者的研究相比,后者没有配置吹扫装置,而是通过改变探头的位置和角度保证[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S采集窗口的清洁。[/align][align=left][color=#231f20]此外,[/color][color=#231f20]Mä rk[/color]等[color=#231f20]则通过一旁路系统进行在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]的采集,由此避免了流化床干燥过程中温度变化对光谱重复性的影响。[/color][/align][align=left] Green等[sup][/sup]研究了探头安装到流化床内进行接触式取样的3种装置对在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S水分预测的准确性的影响,颗粒分别在不同规模的流化床干燥器(65-L,300-L,600-L)中进行实验,并研究使用3种不同的取样装置以提高[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S方法的准确性。研究结果表明过程的不均匀性对表面预测的准确度会产生重要影响,此结论适合于易于不均一化的固体颗粒和混悬液系统的在线测量。此外,Heigl等采用实验室规模流化床研究了不同光谱背景和取样方式对PLS回归模型预测准确度的影响。结果显示透过流化床壁(聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯)采集的在线光谱和透过玻璃瓶采集的离线光谱建立的模型,与去除了此两个背景吸收所建立的模型相比,鲁棒性更好;其次,在线光谱建立的模型,与停止设备后取样采集的离线光谱所建立的模型相比,前者的鲁棒性和预测准确度更佳。[/align][align=left][b]1.2 颗粒的粒径大小[/b][/align][align=left][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S不仅包含样品的化学信息(比如水分含量),而且还包含样品的物理信息,比如,颗粒粒径的不同可产生基线偏移。由此,可以根据光谱的基线偏移来检测颗粒粒径的大小。[/align][align=left]在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S早期用来监测水分含量,但粒径作为质量控制的关键参数,影响压片过程片重均一性、可压性以及脆碎度等,因此为了进一步保证产品质量,提高生产效率,有必要对粒径进行在线监测。在20世纪90年代,相关研究人员对在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S监测颗粒粒径的变化进行了初期探索。Frake等[sup][color=black][/color][/sup][color=black]在生产规模顶喷制粒流化床([/color]40-kg)内安装[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光纤探头,用来连续采集颗粒的光谱信息。[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光纤探头安装在偏下流处产品密度较高的位置以保证探头的清洁;研究中用原始光谱信息来表征颗粒粒径的变化,并绘制出2282nm处吸光度值随时间的变化图,其和粒径随时间变化图具有相似性,但由于颗粒变化模型的复杂性,并未能建立[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S粒径定量模型。[color=black]Rantanen[/color][color=black]等[/color][sup][/sup]在流化床制粒机中采用[color=red]四波长检测器[/color][color=black]对不同等级的微晶纤维素进行[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱的采集,其中1740nm和2145nm两波长用于粒径的测定,并利用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S吸光度值区分微晶纤维素的等级。研究中采用激光衍射法测量微晶纤维素的中值粒径,与[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱吸光度值进行关联得到两者的相关性图。[/align][align=left][color=black]Findlay[/color][color=black]等[/color][sup][/sup]在流化床制粒干燥过程中使用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S在线监测颗粒水分含量和粒径大小,并用两者的监测结果结合流化床传质传热特性来判断制粒喷雾终点和颗粒干燥终点。使用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱仪通过流化床上的玻璃窗采集样品光谱,此玻璃窗安装有一个特殊的垫圈以保持窗口的清洁。制粒过程中每隔5 min停机取样进行一级数据的测量,其中用干燥失重法测定样品含水量数据,用图像分析法测量颗粒的粒径大小。此外,样品在湿颗粒状态和干颗粒状态采集的[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱存在差异(由于水对[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱的影响),而且在制粒初期的前10min采集窗易被湿粉末污染,由此,与制粒的早期阶段相比,[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S在接近喷雾结束和干燥阶段更能获得准确的粒径数据。研究结果表明当样品含水量超过3%([i]w/w[/i])时,需要调整粒径的测量值,使得制粒过程中采用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S测得的数据和通过一级方法测得的数据可以较好地吻合。随后对[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]数据进行电脑编程,可以对流化床制粒过程进行程序化控制。同样,Makoto Otsuka等[sup][color=black] [[/color][/sup][sup]20][/sup][color=black]使[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url]透过流化床的玻璃壁采集光谱,并使用定制的橡皮刮刀来保持玻璃壁的清洁,研究了[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S在线监测实验室规模流化床制粒过程粒径和水分的变化。此外,实验分别使用3种不同浓度的粘合剂([color=black]10%[/color][color=black],[/color]8.5%,[color=black]7.5%[/color][color=black]的羟丙基纤维素)溶液,取样后采用筛分法测定样品的[/color]D[sub]50[/sub],用[color=black]PLSR[/color][color=black]方法建立粒径定量模型,结果证明了[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S在流化床混合、制粒和干燥过程预测对乙酰氨基酚配方颗粒水分含量和D[sub]50[/sub]的可行性。[/align][align=left][color=#141314]Nieuwmeyer[/color][color=#141314]等[/color][sup][/sup]用[color=#141314]PLSR[/color][color=#141314]法分别建立了水分含量和粒径的[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]定量模型。采用激光衍射法测得干样品的平均粒径(D[sub]50[/sub])作为一级数据,和干样品的[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱数据关联,建立了具有4个主成分因子的平均粒径PLSR定量模型。Makoto Otsuka等[sup][color=black][[/color][/sup][sup]20][/sup]采用实验室规模的流化床制粒机研究[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S监测制粒过程的粒径和水分变化。[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱仪透过流化床的玻璃壁采集光谱,使用定制的橡皮刮刀来保持玻璃壁的清洁。研究实验分别使用3种不同浓度的粘合剂([color=black]10%[/color][color=black],[/color]8.5%,[color=black]7.5%[/color][color=black]的羟丙基纤维素)溶液,采用筛分法测定样品的[/color]D[sub]50[/sub],对[color=black][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url][/color][color=black]光谱进行[/color]MSC预处理后,采用[color=black]PLSR[/color][color=black]方法建立粒径定量模型,并对模型进行了外部交叉验证。此研究结果证明了[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S在流化床混合、制粒和干燥过程预测对乙酰氨基酚配方颗粒水分含量和D[sub]50[/sub]的可行性,表明[color=black][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S[/color][color=black]可以作为在线实时监测制粒过程的有力工具。[/color][/align][align=left][b][color=#0d0d0d]1.3 [/color]颗粒的堆密度[/b][/align][align=left]制粒过程中除了颗粒含水量和粒径两个关键参数外,颗粒的堆密度也是判断颗粒质量的重要参数,例如,可以通过测量堆密度大小判断颗粒的流动性和可压性。Manel等[sup][/sup]研究在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S在生产规模流化床制粒系统(GLATTWSG300)生产过程中的应用,其不仅在线监测制粒过程中产品水分和粒径的变化,还对颗粒的堆密度进行实时监测。通过[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]反射光纤探头透过流化床制粒机上的玻璃窗采集光谱,采用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱数据建立基于主成分分析的定性多变量分析模型,监测制粒过程,判断制粒的操作环境是否正常以及判断制粒过程是否出现异常。同样,用PLS方法建立了多个定量分析模型来监测制粒过程中各参数的变化(堆密度、含水量、粒径分布),实现了对流化床制粒干燥过程进行实时在线控制。[/align][align=left][b]2 [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]应用于流化床包衣过程[/b][/align][align=left][color=black]流化床包衣广泛用于膜缓控释、骨架缓控释胶囊[/color]、丸剂包衣等。通过包衣可以掩盖药物的不良气味,还可以隔绝空气,避光防潮,提高药物的稳定性;[color=black]此外,合适的薄膜包衣厚度可控制膜的渗透性,使所包药物在体内扩散释放,达到定时、定位给药的目的[/color][sup][/sup],因此在流化床包衣过程中,包衣厚度是其质量控制的重要指标,用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S对此过程进行实时在线监测,可以有效判断包衣终点,提高产品质量。[/align][align=left] 早期Kirsch等[sup][/sup]采用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S对片剂的包衣厚度进行了离线分析,验证了[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S方法可作为快速、无损检测包衣厚度的有效方法。20世纪初期,Andersson等[sup][/sup]把[color=#231f20][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S[/color][color=#231f20]光纤漫反射探头安装到流化床包衣机上,用于包衣过程中包衣厚度的在线监测。每批实验生产的样品量为[/color]0.5 kg,其中,包衣液材料和丸芯材料的化学组成不同,包衣液为乙基纤维素(具有荧光性),包衣厚度的一级测定方法采用图像分析法,通过包衣材料的荧光特性测定包衣厚度。采用Savitzky-Golay15点平滑和二阶导数对光谱进行预处理,选用1100-1250,[color=#231f20]1300-1450[/color][color=#231f20],以及[/color]1600-1800 nm的波长范围(纤维素类有较强的吸收)建立PLS定量模型,模型结果为R[sup]2[/sup]=0.97[color=#231f20],校正均方根误差为[/color]2.2 μm,可以较准确的判断包衣终点。Lee等[sup][/sup]使用平均聚类的方法建立了[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]包衣厚度的动态校正模型,此模型具有较好的预测能力。在流化床包衣过程中在线采集[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱,并间隔一定时间收集样品来测定一级数据(包衣厚度)。为了保证在线光谱的准确性,把对应收集样品时间点的21或[color=#231f20]45[/color][color=#231f20]个光谱取平均,然后与相应的一级数据关联建立[/color]PLS模型,并对模型进行外部验证。结果表明[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]可以作为流化床包衣过程在线监测工具,准确的判断包衣终点。[/align][align=left][color=black]Hudovornik[/color][color=black]等[/color][sup][/sup]采用[color=black][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url][/color][color=black]和空气滤波技术[/color](Spatial Filtering Technique, SFT)[color=black]监测中试流化床底喷包衣过程,建立了[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]水分含量预测模型,并表明[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]实时预测包衣厚度的可能性,此外,评估了两种在线方法判断过程异常(丸芯磨损和沉积)的能力。研究中建立的[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]水分含量模型对包衣液的成分非常敏感,需要控制包衣液成分的变化以及采用合适的校正集范围来获得较好的预测结果。采用在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]光谱和[color=black]SFT[/color][color=black]数据关联建立了[/color]PLS包衣厚度定量模型,此[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]模型建立的物质基础为药物层的主药成分,随着包衣厚度的增加,主药成分的吸收峰(1670nm处)的强度逐渐降低,所以选择了1600-1751nm的波长范围建立此模型。结果表明采用[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]建立的包衣厚度、水分含量定量模型预测能力较好,同样能够实时判断包衣过程的异常状态,因此,表明[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]可以单独作为实时监测包衣过程的在线工具。[/align][align=left][b]3 结论与展望[/b][/align]近年来,随着[color=black]PAT[/color][color=black]在制药行业的推广,[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S技术已被应用到制剂生产的各个过程。流化床制粒和包衣作为制剂的关键环节,对其生产过程进行实时监测,不仅能够优化生产工艺,提高产品质量,还可以节省能源,为制药企业增加效益。本文综述了在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S技术监测流化床制粒和包衣过程的研究进展,目前流化床技术在我国制药行业已得到广泛的应用,启示我们可以对流化床工艺进行在线工程化改造,采用在线[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S实现流化床制粒和包衣过程实时监测,实现生产过程的自动化和智能化控制[color=black],保证产品的[/color]安全、有效、稳定、均一[color=black]。[/color][b][/b][align=left][b]参考文献[/b][/align][align=left] 张东利,郝东升,舒安庆,张维蔚.流化床喷雾造粒技术进展 . 化学工业与工程, 2005, 22(4): 289-295.[/align][align=left]宋顺宗,辛聪,宫国华,郭建鹏.利用流化床制备中药包衣颗粒的工艺研究.时珍国医国药,2007, 18(11): -2715.[/align][align=left]U.S. Food and Drug Administra2714tion. Guidance for Industry PAT-A Frameworkfor Innovative Pharmaceutical Development, Manufacturing and Quality Assurance.New Hampshire Avenue: FDA, 2004. [/align][align=left][color=black]Nä rvä nen T, Seppä lä K, Antikainen O, et al. A newrapid on-line imaging method to determine particle size distribution ofgranules, [i]AAPS Pharm Sci Technol, [/i]2008,9: 282-287.[/color][/align][align=left][color=black]Sandler N. Photometric imaging in particle sizemeasurement and surface visualization [/color][color=#231f20].[/color][i][color=black] Int J Pharm,[/color][/i][color=#231f20] 2011, 417: 227-234.[/color][/align][align=left][color=black]Mož ina M, Tomaž evič D, Leben S, et al. Digitalimaging as a process analytical technology tool for fluid-bed pellet coatingprocess[/color][color=#231f20].[/color][i][color=black]Eur J Pharm Sci, [/color][/i][color=black]2010,44: 156-162.[/color][/align][align=left] [color=black]Alshihabi F,Vandamme T, Betz G. Focused beam reflectance method as aninnovative (PAT) tool to monitor in-line granulation process in fluidized bed.[i]Pharm Dev Technol,[/i] 2011:73-84.[/color][/align][align=left] [color=#231f20]Sheahan T, Briens L. [/color]Passive acoustic emissions monitoring of the coating of pellets ina fluidized bed—A feasibility analysis . [i]PowderTechnol,[/i] 2015, 283: 373-379.[/align]褚小立.化学计量学方法与分子光谱分析技术. 北京:化学工业出版社,2011. 259.[align=left] Alcala M, Blanco M, BautistaM,et al. [color=black]On-line monitoring of a granulationprocess by [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] spectroscopy [/color][color=#231f20].[/color][color=black] [i]J Pharm Sci, [/i]2010,99(01): 336-345.[/color][/align][align=left]刘怡,马怡.流化床制粒影响因素的探讨. 中国医药工业杂志,2004,35(9): 566-568.[/align][align=left][color=black]Kona R, Haibin Qu, Mattes R, et al. Application ofin-line near infrared spectroscopy and multivariate batch modeling for processmonitoring in fluid bed [/color][color=#231f20]granulation . [/color][i][color=black]Int J Pharm,[/color][/i][color=#231f20]2013, 452: 63-72.[/color][/align][align=left][color=black]Rantanen J, [/color]Rasanen E[color=black], [/color]Tenhunen J[color=black], et al.In-line moisture measurement during granulation with a four-wavelength nearinfrared sensor: an evaluation of particle size and binder effects [/color].[color=black] [i]Eur J Pharm Biopharm[/i], 2000, 50: 209-217.[/color][/align][align=left][color=black]Peinado A, Hammond J, Scott A. Development, validationand transfer of a near infrared method to determine in-line the end point of afluidised drying process for commercial production batches of an approved oralsolid dose pharmaceutical product . [i]J Pharm Biomed Anal, [/i]2011,54: 13-20.[/color][/align][align=left] [color=black]Green RL,Thurau G, Pixley NC, et al. In-line monitoring of moisture content in fluid beddryers using near-IR spectroscopy with consideration of sampling effects onmethod accuracy [/color][color=#231f20]. [/color][i][color=black]Anal Chem,[/color][/i] 2005, 77: 4515-4522.[/align][align=left][color=black] Frake P,Greenhalgh D, Grierson SM, et al. Process control and end-point determinationof a fluid bed granulation by application of near infra-red spectroscopy [/color].[i][color=black]Int J Pharm,[/color][/i] 1997,151: 75-80.[/align][align=left][color=black] Rantanen J,Yliruusi J. Determination of particle size in a fluidized bed granulator with anear infrared set-up [/color][color=#231f20].[/color] [i]Pharm Pharmacol Commun[/i],1998,4:73-75.[/align][align=left] Findlay WP, Peck GR, Morris KR. Determination of fluidizedbed granulation end point using near-infrared spectroscopy and phenomenologicalanalysis [color=#231f20]. [/color][i][color=black]J Pharm Sci,[/color][/i] 2005,94: 604-612.[/align][align=left][color=black] NieuwmeyerFJS, Damen M, Gerich A, et al. Granule characterization during fluid bed dryingby development of a near infrared method to determine water content and mediangranule size [/color][color=#231f20]. [/color][i][color=black]Pharm Res[/color][/i], 2007, 24(10): 1854-1861.[/align][align=left] Otsuka M, Koyama A, Hattori Y. Real-time release monitoringfor water content and mean particle size of granules in lab-sized fluid-bedgranulator by near-infrared spectroscopy [color=black]. [i]RSC Adv, [/i]2014, 4: 17461-17468.[/color][/align][align=left] 柯博克[color=black], [/color][color=black]刘雪松[/color], 陈勇[color=black], [/color][color=black]等[/color].[color=black][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]快速测定复方丹参滴丸的包衣厚度[/color][color=black].[/color]复方丹参滴丸论文集[color=black],2005-2010:487-490.[/color][/align][align=left] Kirsch JD, Drennen JK. Near-infrared spectroscopy monitoringof the filming coating process [color=#231f20][/color]. [i]Pharm Res,[/i] 1996,13(02): 234-237.[/align][align=left] [color=#231f20]Andersson M, FolestadS, Gottfries J, et al. Quantitative analysis of film coating in a fluidized bedprocess by in-Line [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] spectrometry and multivariate batch calibration [/color]. [i]Anal Chem, [/i]2000, 72:2099-2108.[/align][align=left] [color=#231f20]Lee MJ, Park CR, KimAY, et al. Dynamic calibration for the in-Line [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] monitoring of film thicknessof pharmaceutical tablets processed in a fluid-bed coater . [i]J Pharm Sci,[/i] 2010, 99(01): 325-335.[/color][/align][align=left] [color=#231f20]Lee MJ, [/color]Seo DY, [color=#231f20]Lee HE, etal. In line [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] quantification of film thickness on pharmaceutical pelletsduring a fluid bed coating process [/color][color=black].[/color][i]Int J Pharm[/i][color=black], 2011, 403:66-72.[/color][/align][align=left] [color=black]Hudovornik G, Korasa K, Vre[/color]č [color=black]er F. [/color]A study on the applicability of in-line measurements in themonitoring of the pellet coating process [color=black]. [i]Eur J Pharm Sci[/i], 2015, 75: 160-168.[/color][/align][align=left][color=black] [/color][/align]
X射线对人体组织能造成伤害。人体受X射线辐射损伤的程度,与受辐射的量(强度和面积)和部位有关,眼睛和头部较易受伤害。 衍射分析用的X射线(属“软”X射线)比医用X射线(属“硬”X射线)的波长长,穿透弱,吸收强,故危害更大。所以,每个实验人员都必须牢记:对X射线“要注意防护!”。人体受超剂量的X射线照射,轻则烧伤,重则造成放射病乃至死亡。因此,一定要避免受到直射X射线束的直接照射,对散射线也需加以防护,也就是说,在仪器工作时对其初级X射线(直射线束)和次级X射线(散射X射线)都要警惕。前者是从X射线焦点发出的直射X射线,强度高,它通常只存在于X射线分析装置中限定的方向中。散射X射线的强度虽然比直射X射线的强度小几个数量级,但在直射X射线行程附近的空间都会有散射X射线,所以直射X射线束的光路必需用重金属板完全屏蔽起来,即使小于1mm的小缝隙,也会有X射线漏出。 防护X射线可以用各种铅的或含铅的制品(如铅板、铅玻璃、铅橡胶板等)或含重金属元素的制品,如含高量锡的防辐射有机玻璃等。 按照X射线防护的规定,以下的要求是必须遵守的: 1. 每一个使用X射线的单位须向卫生防疫主管部申请办理“放射性工作许可证”和“放射性工作人员证”;负责人需经过资格审查。 2. X射线装置防护罩的泄漏必须符合防护标准的限制:在距机壳表面外5cm处的任何位置,射线的空气吸收剂量率须小于2.5μGy/小时(Gy -戈瑞,吸收剂量单位)。在使用X射线装置的地方,要有明确的警示标记,禁止无关人员进入。 3. X射线操作者要使用防护用具。 4. X射线操作者要具备射线防护知识,要定期接受射线职业健康检查,特别注意眼、皮肤、指甲和血象的检查,检查记录要建档保存。 5. X射线操作者可允许的被辐照剂量当量定为一年不超过5雷姆或三个月不超过3雷姆(考虑到全身被辐照的最坏情况而作的估算)。 请参照以下标准: GB4792 — 84 《放射卫生防护基本标准》 GB8703 — 88 《辐射防护规定》 GWF01 — 88 《放射工作人员健康管理规定》
X射线对人体组织能造成伤害。人体受X射线辐射损伤的程度,与受辐射的量(强度和面积)和部位有关,眼睛和头部较易受伤害。 衍射分析用的X射线(属“软”X射线)比医用X射线(属“硬”X射线)的波长长,穿透弱,吸收强,故危害更大。所以,每个实验人员都必须牢记:对X射线“要注意防护!”。人体受超剂量的X射线照射,轻则烧伤,重则造成放射病乃至死亡。因此,一定要避免受到直射X射线束的直接照射,对散射线也需加以防护,也就是说,在仪器工作时对其初级X射线(直射线束)和次级X射线(散射X射线)都要警惕。前者是从X射线焦点发出的直射X射线,强度高,它通常只存在于X射线分析装置中限定的方向中。散射X射线的强度虽然比直射X射线的强度小几个数量级,但在直射X射线行程附近的空间都会有散射X射线,所以直射X射线束的光路必需用重金属板完全屏蔽起来,即使小于1mm的小缝隙,也会有X射线漏出。 防护X射线可以用各种铅的或含铅的制品(如铅板、铅玻璃、铅橡胶板等)或含重金属元素的制品,如含高量锡的防辐射有机玻璃等。 按照X射线防护的规定,以下的要求是必须遵守的: 1. 每一个使用X射线的单位须向卫生防疫主管部申请办理“放射性工作许可证”和“放射性工作人员证”;负责人需经过资格审查。 2. X射线装置防护罩的泄漏必须符合防护标准的限制:在距机壳表面外5cm处的任何位置,射线的空气吸收剂量率须小于2.5μGy/小时(Gy -戈瑞,吸收剂量单位)。在使用X射线装置的地方,要有明确的警示标记,禁止无关人员进入。 3. X射线操作者要使用防护用具。 4. X射线操作者要具备射线防护知识,要定期接受射线职业健康检查,特别注意眼、皮肤、指甲和血象的检查,检查记录要建档保存。 5. X射线操作者可允许的被辐照剂量当量定为一年不超过5雷姆或三个月不超过3雷姆(考虑到全身被辐照的最坏情况而作的估算)。 请参照以下标准: GB4792 — 84 《放射卫生防护基本标准》 GB8703 — 88 《辐射防护规定》 GWF01 — 88 《放射工作人员健康管理规定》
[font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]流化床工艺生产中[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]数据采集[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]实验方案设计[/b][/size][/font][size=14px]本实验所用的是山东新马制药装备有限公司生产的[/size][size=14px]LGL002[/size][size=14px]实验型流化床。物料的用量要根据底锅的大小和喷枪的位置决定。最少物料量要使得物料在底锅内填充的高度高于近红外探头孔的高度;最大物料量要保证物料在流化的过程中,大部分物料被进口空气吹起来的高度不得超过喷枪,否则会使得大部分物料喷不到粘合剂。经过设计,每批次制粒的总重量为[/size][size=14px]1500g[/size][size=14px]。其中,对乙酰氨基[/size][size=14px]酚[/size][size=14px]75g[/size][size=14px],乳糖[/size][size=14px]495g[/size][size=14px],淀粉[/size][size=14px]375g[/size][size=14px],微晶纤维素[/size][size=14px]555g[/size][size=14px],配制浓度为[/size][size=14px]3%[/size][size=14px]的羟丙基甲基纤维素作为制[/size][size=14px]粒过程[/size][size=14px]中的粘合剂。[/size][size=14px]为了找到制[/size][size=14px]粒过程[/size][size=14px]中流化床的工艺参数与颗粒水分含量的关联关系,首先需要通过实验的方法来确定制[/size][size=14px]粒过程[/size][size=14px]中工艺参数的可行区间。进风量的大小主要取决于物料的实际状态,进风的最小量要使得物料处于良好的流化状态,进风的最大量要根据吹起物料的高度,即还是要满足不得超过喷嘴高度的原则。最终获得风机开启比例为[/size][size=14px]20%~30%[/size][size=14px],风量的大小范围为[/size][size=14px]30m[/size][font='times new roman'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][size=14px]/h~60m[/size][font='times new roman'][size=14px]3[/size][/font][size=14px]/h[/size][size=14px]。雾化压力与蠕动泵流量大小会影响喷出的粘合剂,合适大小的雾化压力和蠕动泵蠕动泵流量可以保证喷嘴喷出的粘合剂呈雾状。物料温度主要与进风温度、蠕动泵流量有关,物料温度的大小可以从侧面反应物料中水分含量的多少,物料的温度越高,水分在温度作用下蒸发的就越快,使物料的含水量就较低。以物料温度最高[/size][size=14px]40[/size][size=14px]℃[/size][size=14px]为标准,调整蠕动泵流量和进风温度,得到蠕动泵流量和进风温度的设计区间。[/size][size=14px]在制粒前,首先对流化床进行预热处理[/size][size=14px]15[/size][size=14px]分钟,蒸干流化[/size][size=14px]床内部[/size][size=14px]残留的水分。放入配制好的物料进行混合[/size][size=14px]5[/size][size=14px]分钟,继续加热至物料温度达到[/size][size=14px]40[/size][size=14px]℃[/size][size=14px],打开蠕动[/size][size=14px]泵开始[/size][size=14px]喷入粘合剂。对蠕动泵流量和进风温度进行设定,得到失败批次中工艺参数的极限值。蠕动泵流量和进风温度的参数区间设计过程如下图所示。[/size]最终设定蠕动泵流量的参数设计区间为3.75~14.25ml/min,进风温度的参数设计区间在50℃~70℃。流化床所有可以操作的工艺参数可操作范围如下表所示。[align=center][font='times new roman'][size=16px]工艺参数操作空间[/size][/font][/align][table][tr][td][align=center][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]进风量[/size][size=13px]/[/size][size=13px]m[/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px]3[/size][/font][size=13px][/size][size=13px]h[/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px]-1[/size][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]进风温度[/size][size=13px]/[/size][size=13px]℃[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]蠕动泵流量[/size][size=13px]/ml[/size][size=13px][/size][size=13px]min[/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px]-1[/size][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]雾化压力[/size][size=13px]/bar[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]最小值[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]30[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]50[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]3.75[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]0.8[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]最大值[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]60[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]70[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]14.25[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1.8[/size][/align][/td][/tr][/table][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]水分数据采集[/b][/size][/font][size=14px]颗粒的实际水分数据需要对颗粒离线测量进行采集,常用的测量方法是干燥失重法。[/size][size=14px]实验仪器为水分含量测试仪([/size][size=14px]xy-102[/size][size=14px])。先称量取样瓶的重量为[/size][size=14px][i]M[/i][/size][size=14px],在制[/size][size=14px]粒过程[/size][size=14px]中通过取样瓶从取样口取出少量样品进行称重得到重量为[/size][size=14px][i]M[/i][/size][font='times new roman'][size=14px][i]1[/i][/size][/font][size=14px],将样品倒入水分含量测试仪中的托盘上进行干燥,直到样品重量不再变化。把干燥后的样品重新倒入之前的取样瓶中进行称重得到重量为[/size][size=14px][i]M[/i][/size][font='times new roman'][size=14px][i]2[/i][/size][/font][size=14px]。计算[/size][size=14px][i]M[/i][/size][font='times new roman'][size=14px][i]1[/i][/size][/font][size=14px]和[/size][size=14px][i]M[/i][/size][font='times new roman'][size=14px][i]2[/i][/size][/font][size=14px]的之间的差值,求出样品中的水分含量。水分含量计算公式如下:[/size][align=right][size=14px] [/size][size=14px] [/size] (1)[/align]实验中使用的水分含量测试仪器如下图所示。[align=center][font='times new roman'][size=16px]图[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]颗粒水分含量测试仪[/size][/font][/align][size=14px]制[/size][size=14px]粒过程[/size][size=14px]中每隔[/size][size=14px]4[/size][size=14px]分钟去取一次样品,每批次的制[/size][size=14px]粒时间[/size][size=14px]为[/size][size=14px]60[/size][size=14px]分钟,如此每个批次采集[/size][size=14px]15[/size][size=14px]个样品,进行了六批实验总共取得了[/size][size=14px]90[/size][size=14px]个样品的重量数据。用式([/size][size=14px]2-1[/size][size=14px])对每个样品进行水分含量的计算。得到[/size][size=14px]90[/size][size=14px]个样品的含水量如下表所示。[/size][align=center][font='times new roman'][size=16px]表[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]样品水分含量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]数据[/size][/font][/align][table][tr][td][align=center][font='宋体'][size=13px]序号[/size][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='宋体'][size=13px][color=#000000]瓶重[/color][/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=13px][color=#000000]/[/color][/size][/font][size=13px][color=#000000][i]M[/i][/color][/size][size=13px][color=#000000]g[/color][/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px][color=#000000]-1[/color][/size][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='宋体'][size=13px]样品重[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=13px]/[/size][/font][size=13px][color=#000000][i]M[/i][/color][/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px][color=#000000][i]1[/i][/color][/size][/font][size=13px][color=#000000]g[/color][/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px][color=#000000]-1[/color][/size][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='宋体'][size=13px]干燥后重量[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=13px]/[/size][/font][size=13px][color=#000000][i]M[/i][/color][/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px][color=#000000][i]2[/i][/color][/size][/font][size=13px][color=#000000]g[/color][/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px][color=#000000]-1[/color][/size][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='宋体'][size=13px]水分[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=13px][color=#000000]/[/color][/size][/font][size=13px][color=#000000]g[/color][/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='宋体'][size=13px][color=#000000]含水率/[/color][/size][/font][size=13px][color=#000000]%[/color][/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]1[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]18.9363[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]21.1395[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]21.0396[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]0.0999[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]4.53[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]2[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]18.9028[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]21.193[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]21.1154[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]0.0776[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]3.39[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]3[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]17.9725[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]20.1945[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]20.1151[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]0.0794[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]3.57[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]4[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]19.5796[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]21.5691[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]21.4839[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]0.0852[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]4.28[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]…[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]…[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]…[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]…[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]…[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]…[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]88[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]19.8203[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]21.9924[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]21.8896[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]0.1028[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]4.73[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]89[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]17.6107[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]19.84[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]19.7914[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]0.0486[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]2.18[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]90[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]16.5792[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]18.6692[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]18.6366[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]0.0326[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1.56[/size][/align][/td][/tr][/table][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]光谱数据采集[/b][/size][/font][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]是由于分子通过能量跃迁的方式产生的,对含H基团的N-H、C-H、O-H等化学键有很强的吸收峰[font='times new roman'][size=16px][51][/size][/font]。[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]对含有H元素的光谱中心带近似位置见下表。[align=center][font='times new roman'][size=16px]表[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]H[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]元素[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]中心带近似位置[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](nm)[/size][/font][/align][table][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]振动类型[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]N-H[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]C-H[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]O-H[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]H[/size][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2[/size][/font][size=13px]O[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]伸缩基频[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]3000[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]3[/size][size=13px]300[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]2[/size][size=13px]700[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]2[/size][size=13px]700[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]剪式弯曲[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]6452[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]6[/size][size=13px]700[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]6[/size][size=13px]250[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]6[/size][size=13px]250[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]合频[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]2200[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]2[/size][size=13px]300[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]2[/size][size=13px]000[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1[/size][size=13px]940[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]二级倍频[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1540[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1[/size][size=13px]745[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1[/size][size=13px]450[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1[/size][size=13px]440[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]三级倍频[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1040[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]1[/size][size=13px]170[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]9[/size][size=13px]50[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]9[/size][size=13px]60[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]四级倍频[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]800[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]9[/size][size=13px]00[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]7[/size][size=13px]40[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]7[/size][size=13px]50[/size][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][size=13px]五级倍频[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]—[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]7[/size][size=13px]50[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]—[/size][/align][/td][td][align=center][size=13px]—[/size][/align][/td][/tr][/table][size=14px]水是由[/size][size=14px]H[/size][size=14px]和[/size][size=14px]O[/size][size=14px]元素组成的,因此,利用近红外光可以较为准确地预测出含有[/size][size=14px]O-H[/size][size=14px]化学键的水分含量。在每次取样的时候用近红外探头对样品进行扫描来取得每个样品的原始光谱。光谱采集软件用的是[/size][size=14px]MicroNIR[/size][size=14px]™ Pro v2.5.1[/size][size=14px]软件,首先对空气进行采谱,然后用聚四氟乙烯制成的白板挡住探头采集背景光谱进行校准,最后将探头伸入流化床腔体中对样品进行采谱。通过探头采集到的[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]共有[/size][size=14px]125[/size][size=14px]个波段,波长的范围在[/size][size=14px]908.1nm~1676.0nm[/size][size=14px]之间。图为通过采样得到的[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]。[/size][align=center][font='times new roman'][size=16px]图[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]图[/size][/font][/align][size=14px]从图中可以看出,在[/size][size=14px]1400nm~1650nm[/size][size=14px]波段之间[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]的吸收度比较高,并且在不同水分含量间变化比较明显。[/size][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]工艺参数数据采集[/b][/size][/font][size=14px]制[/size][size=14px]粒过程[/size][size=14px]中的工艺参数主要包括物料温度、进风温度、排风温度、蠕动泵流量、雾化压力和进风量。为了探究流化床工艺参数和颗粒水分含量间的关系模型,必须对制[/size][size=14px]粒过程[/size][size=14px]中的工艺参数进行实时采集。各种传感器对工艺参数数据进行采集并进行数字化,通过串口的方式将参数[/size][size=14px]数[/size][size=14px]据传到流化床的操作屏幕上,并以时间戳的形式将参数数据保存在用于记录生产过程的[/size][size=14px]U[/size][size=14px]盘中。工艺参数数显屏幕如下图所示。[/size][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009031751133116_6034_3890113_3.jpeg[/img][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]小[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]结[/b][/size][/font][size=14px]本文[/size][size=14px]对流化床制粒过程中的数据采集进行了研究,主要结论如下:[/size][size=14px]([/size][size=14px]1[/size][size=14px])为了能获取流化床制粒过程中颗粒的水分含量和工艺参数数据,建立了流化床制粒过程数据采集平台。[/size][size=14px]([/size][size=14px]2[/size][size=14px])设计了制[/size][size=14px]粒过程[/size][size=14px]的试验方案,进行了[/size][size=14px]6[/size][size=14px]个批次的实验,利用干燥失重法采集到了[/size][size=14px]90[/size][size=14px]个颗粒水分数据。对这[/size][size=14px]90[/size][size=14px]个样品进行近红外采谱,为建立水分预测模型奠定了数据基础。[/size]
最近被氨水熏得不行,主要是熏眼睛,想买个眼罩,不知道什么比较好,老板比较抠门。。
[align=center][color=#191919]如何在流化床包衣过程中实现智能制造[/color][/align]当前中国制造由大变强的序幕已经拉开,[color=#191919]“[/color][color=#191919]中国制造[/color][color=#191919]2025”[/color][color=#191919]和[/color][color=#191919]“[/color][color=#191919]工业[/color][color=#191919]4.0”[/color][color=#191919]正在促进一场新工业变革的到来。[/color][color=#070707]推进智能制造,能够有效缩短产品研制周期,提高生产效率和产品质量,降低运营成本和资源能源消耗,加快发展智能制造,对于提高制造业供给结构的适应性和灵活性、培育经济增长新能动都具有十分重要的意义。[/color][color=black]面临新一轮科技变革和产业变革,美国、德国等制造强国纷纷提出了制造业升级的思路和规划。而在[/color][color=black]“[/color]中国制造[color=black]2025”[/color]规划中,智能制造是主攻方向,是未来制造业发展的重大趋势和核心内容,也是解决我国制造业由大变强的根本路径。[color=#191919]智能制造的载体是智能工厂,核心是关键环节智能化,基础是信息物理系统,支撑是工业互联网。智能制造最后带来的效果是生产效率的提升,产品质量的提升,产品研发时间的下降,运营成本的下降,资源能源消耗下降。本文就如何在流化床包衣过程中实现智能制造,以包衣厚度的测量为例,结合[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]等技术,比较几种测量方法的优缺点,结果证明:基于[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]技术的测量方法最为有效,可用于工业化大生产,契合智能制造的理念。[/color][color=black]流化床是指用自下而上快速吹入的气流(进风),穿过固定颗粒,并维持固体颗粒处于不断往复运动状态而形成的固体颗粒床[/color][sup][color=black][/color][/sup][color=black]。[/color]流化床制粒设备目前广泛应用于药品生产过程中,优点显著,该方法是集混合、制粒、干燥、包衣在一个全封闭容器中进行操作的技术,与其它包衣技术相比,具有工艺简单、操作时间短、劳动强度低等特点。目前流化床包衣技术正得到越来越广泛的应用,国内外生产的流化机器的差距也越来越小,这项技术对我国药品生产现代化的发展意义重大。[color=black]此外,[/color]流化床包衣技术具有传质快、传热效率高、流动性好、压缩成型性好等优点。颗粒间较少或几不发生可溶性成分迁移,减小了由此造成片剂含量不均匀的可能性。[color=#191919]包衣是一门将聚合物包裹在固体剂型外形成衣膜的技术,有助于传递药物剂型的许多优势[/color][sup][color=black][/color][/sup][color=#191919]。比如,掩盖片芯中成分的气味,提高物质的稳定性,使药物制剂更加美观,更加干净,并且能够调节药物的释放使药物到达体内再开始释放。药物的包衣使消费者识别和吞咽药物变的更加容易。对于许多制造商来说,包衣可以帮助减少灰尘,并且可以改善药片的机械强度使之经得住触碰,不易破碎。包衣的厚度和均匀性是包衣药物质量好坏的重要指标。研究包衣的厚度对优化包衣设备和工艺有重要的意义。[/color][color=#191919]显微图像测量法[/color][sup][/sup]:[color=#191919]1[/color]、获取药物切片截面。首先,将待测包衣药物切片,切片表面的平整性对包衣厚度的测量至关重要;[color=#191919]2[/color]、显微镜的调节。把切片界面放在显微镜下,调节显微镜的放大倍数和相对位置;[color=#191919]3[/color]、图像传送。用高清数码相机拍摄切片显微图像,并传送至计算机中;[color=#191919]4[/color]、成像测量。在计算机的显示器中显示药片显微图像,利用[color=#191919] Image-Pro Plus [/color][color=#191919]图像处理分析软件标定,并测量包衣的厚度。[/color][color=#191919]拉曼光谱法[/color][sup][/sup]:拉曼光谱法是一种利用激光照射被检测位置发生散射现象,产生与入射光频率不同的散射光谱所进行的分析方法。利用拉曼光谱技术检测灵敏度高,样品基本无需制备,分析速度快,时间短,对样品无接触,无损伤,具有高空间分辨率,以及高光谱分辨率,并且不会对样品造成化学性的,机械的,光化学和热的分解。从检测假冒药品到检测活性物的含量,再到过程分析制造,拉曼光谱技术被广泛应用于生物医学,药物学,文物考古和法庭科学等诸多方面。[color=#191919]测试方法为:激光通过显微镜头聚焦到样品测试点,激发拉曼信号,再由显微镜头收集拉曼信号并传递到光谱仪系统,只要适当控制激光功率密度,热效应不至于破坏样品测试点,可以保证被测样品的完好和信号的真实。[/color][color=#191919]X [/color]射线荧光光谱法:特征[color=#191919] X[/color]射线经过探测器在不同的衍射角上检测,经电路放大,转变为脉冲信号,收集和显示谱线,最后由计算机采集,分析处理谱线。每种元素的原子本身具有独特的电子排列,对于给定特征的[color=#191919] X [/color]射线,能量取决于该原子的原子序数。不同的样本材料会产生不同能量的[color=#191919] X [/color]射线荧光,测定谱线的波长,得到样本中包含的元素,测定谱线的强度,得到该元素的含量,从而确定样本材料的特性,测定包衣的厚度。[color=#191919]太赫兹光谱法:太赫兹成像技术在药物分析以及无损检测等方面有着十分广泛的应用,可以为拉曼成像,[/color][color=#191919]X [/color]射线荧光成像,核磁共振成像以及红外成像提供补充。它可以在不破坏药片包衣的前提下,对包衣的结构情况和包裹情况进行检测分析,并通过传感器进行记录。检测的原理是根据脉冲时间的不同,药片包衣的空腔或微小的异物都可能使太赫兹射线脉冲照射的时间长短发生变化,从而确定包衣的厚度,并且可以检测量化包衣的缺陷和厚度分布。[color=black]近红外([/color][color=black][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url][/color][color=black])在线检测技术:[/color][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]是介于可见光和中红外光之间的电磁辐射波,具备无损、快速、多参数测定、无污染和可在线分析等优点[sup][color=black][/color][/sup][color=#191919],近年来被广泛应用于农业及制药行业中,其中在制药领域,包括制剂过程控制,成品药分析,药品真伪鉴定等多个方面的应用,大大减少了工作量,提升了经济效益。[/color][color=black][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S [/color]是采用近红外的方法直接分析液体、固体粉末、半固体、胶状等多种物态样品,使实验室和工厂的产品分析实现在线化,在几秒钟得到待测参数,与反馈控制技术连用则实现生产过程的在线控制技术[sup][color=black][/color][/sup][color=black]。[/color][color=black]它克服了传统离线分析技术样品预处理复杂以及分析结果滞后的缺陷。[/color][color=black]该方法具有预处理简单、分析速度快、非破坏性及适合于在线分析等优点,在药物的定性鉴别、定量分析及质量控制等方面显示了很大的作用[/color][sup][color=black][/color][/sup][color=black]。[/color][color=black]药品质量与生产过程中的每个环节密切相关。[/color]制药过程关键工艺的监测、控制对于保证药品质量至关重要。[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]分析技术在药物的在线检测方面显示了巨大的优势。[color=#191919]带光纤探头的[/color][color=#191919] [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] [/color][color=#191919]漫反射光谱仪使用[/color][color=#191919] PLS [/color][color=#191919]模式可以对包衣层进行检测。[/color][color=#191919]已发现微丸样品[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]的变化与包衣的厚度之间存在相关性。[/color]在用乙基纤维素[color=#191919](EC)[/color]或羟丙基纤维素[color=#191919](HPMC)[/color]进行包衣的过程中,按一定的时间间隔取样,测定样品的[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url][sup][color=black][/color][/sup][color=#191919]。[/color][color=#191919]采用二阶导数变换和多元散射校正两种方法对光谱进行处理,然后用主成分分析建立计算包衣厚度的校正模型。[/color]再测定样品的溶出度,考察包衣厚度与溶出度的相关性,从而进行生产工艺的监控。[color=#191919]分析以上方法可知,直接用光学显微镜测量药片横截面的厚度相当的费时费力,但是通常能够得到精确的包衣层厚度的数据。[/color][color=#191919]X [/color]射线荧光光谱法操作快速方便,不受样本大小和形状的限制,但灵敏度偏低。拉曼光谱法与[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]法相比,灵敏度更高,但是出现误差的可能性更大。[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]法不需要在测量前进行大量复杂的处理,能够节省分析的时间。是最有效的方法,测量简单并且快速,能够基本实现对物体的快速无损检测。[color=#191919]相比其他技术手段[/color][color=#191919],[/color][color=#191919][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url][/color]在过程控制方面具有快速、无损、样品预处理简单、可以在线监控的优势。可以细致地分析每个技术环节,为先进的理论提供充足的基础资料。[color=#191919]“[/color]质量源于设计([color=#191919]QbD[/color])[color=#191919] ”[/color]以及实时参数放行的理念也要求使用更先进的分析工具帮助人们加深对生产过程的理解,以便设计出更合理的药物生产工艺路线。所以在药品生产过程中,[color=#191919][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url][/color]将会逐步普及,并成为一项常规的质量检测手段为人们的用药安全提供坚实的保障,为智能制造的早日实现作出重要的贡献。[color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color][color=#191919] [/color]参考文献[color=black] [/color]Naidu [i]et al.[/i] [color=black]PAT-BasedControl of Fluid Bed Coating Process Using [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] Spectroscopy to Monitor theCellulose Coating on Pharmaceutical Pellets [/color]. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2016,1149(5): 56-65. Snezana Markovica , Ksenija Poljanec, Janez Kerc [i]et al[/i]. In-line [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] monitoring of keycharacteristics of enteric coated pellets . EUR J PHARM BIOPHARM, 2014, 843(19): 170-174. Min-Jeong Lee, Da-Young Seo, Hea-Eun Lee[i] et al[/i].In line [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] quantification of film thickness on pharmaceuticalpellets during a fluid bed coating process. [color=#333333]INT J PHARM[/color], 2011, 29(9): 2471-2477. 陆庆华, 陈玉洁,严盈富.薄膜包衣厚度测量方法分析.南昌航空大学学报, 2014, 40(8): 1207-1212. 倪力军,朱静,张立国.[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]法测定缓释制剂中冰片释放量.光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 31(9): 1089-1094. 张振宾, 欧俊杰, 林辉等.[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]分析技术在固体制剂生产中的应用.食品与药品,2013, 14(2): 139-142. Roland Hohl, Otto Scheibelhofer, Elena Stocker. Monitoring of a Hot MeltCoating Process via a Novel Multipoint Near-Infrared Spectrometer .AAPS PharmSciTech, 2017, 137(9): 4114-4118. 王小亮, 傅强, 绳金房等.[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]技术在制药过程分析中的应用进展.西北药学杂志, 2009, 29(12): 464-469.[align=right] 邱素君,何雁,张国松.[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]快速测定柴胡总皂苷肠溶片包衣膜厚度研究.中国药科大学学报,2012,67(7): 78-85.[/align]
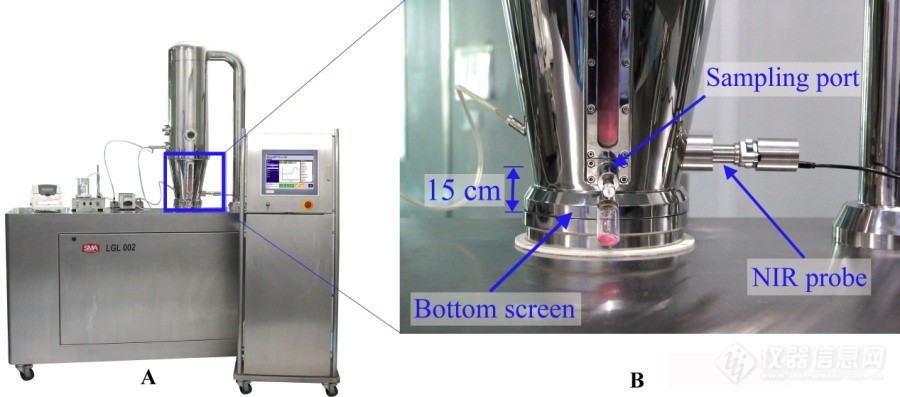
[align=center][font='times new roman'][size=20px][b]流化床混合过程[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=20px][b][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=20px][b]在线监测[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=20px][b]API[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=20px][b]含量[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=20px][b]研究[/b][/size][/font][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px]对小试流化床进行设备改造,将微型[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url]内嵌到流化床腔室中,通过实验设计,将常规流化床混合过程中监测[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]腔[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]室内原料药[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]浓度变化时遇到的变异性来源(原辅料、工艺过程、环境等)尽可能包含进去。采用接触式采集模式进行在线校正集光谱采集,将在线采集到的光谱进行光谱选择,预处理和波段选择,在有限的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]消耗情况下建立定量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]PLS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]模型,最后用外部验证集验证模型的稳定性和预测能力。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px][b]材料[/b][/size][/font][align=left][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]试剂[/b][/size][/font][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px]本文[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]中使用的原辅料及试剂如表。[/size][/font][align=center][font='times new roman']表实验所用试剂及详细信息[/font][/align][table][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman']试剂名称[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']厂家[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']批号[/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman']对乙酰氨基[/font][font='times new roman']酚[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']山东昌达生物科技有限公司[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']190437[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']190438[/font][font='times new roman'],[/font][font='times new roman']190439[/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman']微晶纤维素[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']安徽山河药用辅料股份有限公司[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']180559[/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman']玉米淀粉(药品级)[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']山东聊城华阳医药辅料有限公司[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']18020501[/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman']玉米淀粉(食品级)[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']北京闵松经贸有限公司[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']产品标准号:[/font][font='times new roman']GB31637[/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman']一[/font][font='times new roman']水合乳糖[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']镇江市康富生物工程有限公司[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']20180323[/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman']羟丙基甲基纤维素[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']安徽山河药用辅料股份有限公司[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']180205[/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman']氢氧化钠[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']上海艾览化工科技有限公司[/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman']20190610[/font][/align][/td][/tr][/table][align=left][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]仪器和软件[/b][/size][/font][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px]LGL 002[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]实验型流化床(山东新马制药装备有限公司);[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Micro [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] PAT-U [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]微型[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url](美国[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Viavi[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] Solutions[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]公司);耐高温外接金属探[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]头;紫外分光光度计;烘箱;干燥器;[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]M[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]atlab[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] 2016b[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](美国[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Mathworks[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]公司);[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Unscrambler[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] X 10.4 ([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]挪威[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] CAMO [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]公司[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]) orign85[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](美国[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]OriginLab[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]公司)。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px][b]方法[/b][/size][/font][align=left][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]实验设计[/b][/size][/font][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px]实验设计([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DOE[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])的目的是将流化床混合过程中监测原料药([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])含量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]变化时遇到的变异性来源,包括原辅料理化性质、工艺过程参数、环境参数等尽可能包含进去。对于工艺过程因素,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]通过控制排风机开启的比例,选择了两种不同的进风比例[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](15%[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]25%)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]来[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]模拟在正常混合过程中每个校正集批次通过探头时的动态粉末流动量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]及流动速度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]此外,混合过程中进风温度设定了两个不同的水平,分别为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]50[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]70[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]℃[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],模拟实际混合过程中进风温度的预期范围。对于环境可变性,整个校正集所有混合批次,在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]20%[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]40% RH[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]设置点[/size][/font][font='宋体'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]条件下进行。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]64[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]个校正集批次以全因子的方式设计,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]7[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]个批次和批次[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]共计[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]8[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]个配方批次在两个进风温度设定水平、两个进风量设定点和两个环境湿度设定点条件下完成。[/size][/font][align=left][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]设备改造及在线光谱采集[/b][/size][/font][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px]原始光谱由[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Micro [url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url] PAT-U [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]微型[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url](美国[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Viavi[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] Solutions[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]公司)漫反射模块在线接触式采样方式直接采集,保证了光谱的质量。为了避免温度对光谱仪的影响,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]PAT-U[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]光谱仪连接到一个耐热金属探头上,然后将光谱仪及探头固定在物料车一侧,距底部筛网[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]15[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]cm[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]高,与取样口在同一水平线且垂直于取样口,既不影响在线光谱的采集又保证了用于光谱采集的物料和取出的样品有相同或相似的理化性质。光谱仪探头的蓝宝石窗口附近配有吹扫装置,在光谱采集过程中,每[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]30[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]s[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]对采集窗口进行一次吹扫,防止其被物料覆盖或者污染[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][color=#080000][67, 68][/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]详细信息如图所示。[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]每[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]s[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]自动采集一次,波长范围为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]908.1 nm-1676.0 nm[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],每张光谱平均扫描[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]100[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]次。[/size][/font][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009170817236006_4126_3890113_3.png[/img][align=center][font='times new roman']图[/font][font='times new roman']A[/font][font='times new roman']流化床混合系统设备图[/font][font='times new roman'];[/font][font='times new roman']B[/font][font='times new roman'][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url]及探头的位置[/font][/align][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]一级数据的测定[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]每个混合批次按经验预混合[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]5[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]min[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]至基本均匀后,进行在线光谱采集。光谱采集的同时进行取样,每次[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]取样约[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]3[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]g[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]64[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]个校正集批次共收集[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]64[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]个样品。水分含量的测定采用药典规定的干燥失重法[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]LOD[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][color=#080000][69][/color][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],在烘箱中完成。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量的测定[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]用[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]UV[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]法[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]模型的建立[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]通过实验设计,在实验模拟型流化床上用有限的物料采集到不同工艺参数、不同环境条件下的校正集光谱,用于建立[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]PLS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]定量分析模型。然后,通过不同的光谱选择方法消除异常光谱的干扰。为了进一步提高模型的预测能力,对光谱选择处理后的校正集光谱进行预处理和波段选择,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]通过交互验证均方根误差[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Root Mean Squares Error of Cross-validation[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]RMSECV[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]对校正集模型进行评价。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]此外,外部独立验证集光谱在中试流化床上进行采集,对独立测试集光谱进行诊断分析,来验证模型的稳健性以及在小试实验型流化床上采集校正集光谱的适宜性,以便随后应用于生产型流化床混合过程中。进一步对近红外预测数据和参考值进行方法学考察,探究方法[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]学结果[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的准确性、精密度等用于检测流化床混合过程中潜在的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]瞬态干扰。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][b]模型评价与验证[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]图为优化后的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]PLS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]模型前三个潜在变量([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]LV[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])的二维得分图。如图所示,第一个[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]LV[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]解释了大部分的浓度变异性,第二个[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]LV[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]解释了大部分湿度的变化,第三个[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]LV[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]解释了大部分由进风温度引起的变化。同时,得分图中同一工艺和环境条件下,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]单簇样品[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]点出现的变异代表了[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]DOE[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]中配方的变化,这些变化来源于不同的原料药批次、辅料[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]1[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和辅料[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]的不同比例以及流化床腔室中物料粒径的不同。[/size][/font][table][tr][td][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009170817240488_6697_3890113_3.png[/img][/align][/td][td][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009170817241999_544_3890113_3.png[/img][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman'][b]([/b][/font][font='times new roman'][b]a)[/b][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman'][b]([/b][/font][font='times new roman'][b]b)[/b][/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009170817242568_3144_3890113_3.png[/img][/align][/td][td][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009170817243942_1268_3890113_3.png[/img][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman'][b]([/b][/font][font='times new roman'][b]c)[/b][/font][/align][/td][td][align=center][font='times new roman'][b]([/b][/font][font='times new roman'][b]d)[/b][/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td=2,1][align=center][font='times new roman']图[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']优化后的[/font][font='times new roman']PLS[/font][font='times new roman']模型在前三个潜在变量[/font][font='times new roman'](LV)[/font][font='times new roman']的得分图。图[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']a)[/font][font='times new roman'] (LV1 [/font][font='times new roman'][i]vs[/i][/font][font='times new roman'] LV2)[/font][font='times new roman']中的多种颜色代表了[/font][font='times new roman']API[/font][font='times new roman']含量的分类;[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']b)[/font][font='times new roman'] (LV1 [/font][font='times new roman'][i]vs[/i][/font][font='times new roman'] LV2)[/font][font='times new roman']中多种颜色代表了环境湿度的分类;[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']c) [/font][font='times new roman'](LV1 [/font][font='times new roman'][i]vs[/i][/font][font='times new roman'] LV3)[/font][font='times new roman']中多种颜色代表了[/font][font='times new roman']API[/font][font='times new roman']含量的分类;[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']d)[/font][font='times new roman'] (LV1 [/font][font='times new roman'][i]vs[/i][/font][font='times new roman'] LV3) [/font][font='times new roman']多种颜色代表进风温度的分类[/font][/align][/td][/tr][/table][font='times new roman'][size=16px]校正集中包涵了多种变量因素条件下采集的光谱,(包括工艺因素、环境因素和配方因素)提高了模型对后续实际应用中原辅料、过程和环境变化的稳定性。最后,对模型进行诊断和验证,验证集四批实验[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]每个[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]理论含量配方进行一批实验[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]在低的环境湿度和[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]50℃[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]进风温度条件下完成。图为校正集光谱诊断[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]断[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]图[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]即[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][i]F[/i][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][i]vs[/i][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]Hotelling[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px] [/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][i]T[/i][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和得分图(包含校正集和验证集)表明,校正集和独立外部预测集光谱都在[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]95%[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]置信范围内,再次证明了模型的稳定性和可靠性,证明了近红外技术可用于流化床混合过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量监测的稳定性。进一步对近红外预测数据和参考值进行方法学考察,近红外测量具有良好的准确度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](RMSEP=2.3629%)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]、精密度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](100%[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量下的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]SD=4.8%)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和线性度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](R=0.903)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],说明了[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]法在线监测[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量的可行性。[/size][/font][table][tr][td][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009170817244561_5080_3890113_3.png[/img][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman'][b]([/b][/font][font='times new roman'][b]a)[/b][/font][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][img]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2020/09/202009170817245752_7165_3890113_3.png[/img][/align][/td][/tr][tr][td][align=center][font='times new roman'][b]([/b][/font][font='times new roman'][b]b)[/b][/font][/align][/td][/tr][/table][font='times new roman']图[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman'](a) [/font][font='times new roman']校正集光谱诊断图[/font][font='times new roman']([/font][font='times new roman']即[/font][font='times new roman'][i]F[/i][/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman'][i]vs[/i][/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman']Hotelling[/font][font='times new roman'] [/font][font='times new roman'][i]T[/i][/font][font='times new roman'][size=13px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman'])[/font][font='times new roman']和[/font][font='times new roman'] ([/font][font='times new roman']b) [/font][font='times new roman']得分图(包含校正集和[/font][font='times new roman']验证集)[/font][font='times new roman'][size=18px][b]小结[/b][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]本章节对小试流化床进行设备改造,将微型[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱仪[/color][/url]内嵌到流化床腔室中,通过实验设计,考察了流化床混合过程中影响原料药([/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px])含量的变异性来源,包括原辅料、工艺过程、环境等因素。在有限的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]消耗情况下建立定量[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]PLS[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]模,验证了流化床混合过程[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量在线监测的可行性。采用接触式采集模式进行在线校正集光谱采集,保证了光谱的质量。另外,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]提出并研究了不同的光谱选择方法以提高模型的预测能力,其中余弦距离法效果最好。余弦距离法是一种非常普遍的光谱选择方法,可作为一种优化方法对其他动态过程的光谱进行选择。此外,光谱预处理和变量选择方法对模型预测能力的提高也很重要。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]通[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]过研究不同的预处理和波段选择方法提高了模型的预测能力,[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][i]R[/i][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][i]c[/i][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][i]R[/i][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][i]cv[/i][/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]RMSEC[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]RMSECV[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]分别为[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0.957[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]0.954[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2.3103[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]2.3143[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]对[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px][url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]NIR[/color][/url]S[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]方法进行方法学考察,结果表明近红外测量具有良好的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]准确度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](RMSEP=2.3629%)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]、精密度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](100%[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量下的[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]SD=4.8%)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]和线性度[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px](R=0.903)[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px],[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]说明了[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]法在线监测[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量的可行性。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]本研究可作为中试和工业流化床混合过程中微型近红外传感器在线监测的参考,本研究表明[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/1p][color=#3333ff]近红外光谱[/color][/url]法有可能取代传统的测量方法,实现流化床混合过程在线监测,并可将[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]CQA[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]与关键工艺参数相连接,实现固体制剂的智能化生产。[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]下一步研究中,将对离线光谱进行模型转移研究,进一步提高模型的精度、预测能力和稳定性,并将离线模型、在线模型、模型转移后得到的模型用于中试生产中[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]API[/size][/font][font='times new roman'][size=16px]含量的监测。[/size][/font]
我在网上看日本理学ultraX TTR III 衍射仪资料的时候,看到网上相关图片是下面这样的,没射线防护罩。我以为X射线衍射仪都是有防护罩的。想请问一下,这个设备标配有防护罩吗?[img=,429,376]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2019/05/201905162233211620_552_2653735_3.png!w429x376.jpg[/img]
2011年04月08日,加拿大卫生部对中国产供年龄在3~6个月儿童用的安抚奶嘴实施召回。 此次被召回的商品为“Go, Diego, Go! ”(爱探险的迭戈)和“ Dora the Explorer”(探险家朵拉)安抚奶嘴,该产品的通用代码是(UPC):7 74538 11007 ,被召回的安抚奶嘴以一套两件形式出售。 在“Go, Diego, Go! ”(爱探险的迭戈)安抚奶嘴套装中一件有蓝色防护罩和橙色拉环,另一件有白色防护罩和蓝色拉环;在“ Dorathe Explorer”(探险家朵拉)安抚奶嘴套装中一件有粉色防护罩和白色拉环,另一件有白色防护罩和红色拉环。http://www.cirs-group.com/images/stories/tb/cpscalerts/soothing%20pacifier%20recalls.jpg 该安抚奶嘴自2007~2011年在加拿大境内通过Zellers 商店销售。 本次被召回的商品数量约有4800个。 召回原因:经加拿大卫生部检测确认该安抚奶嘴的仿真乳头和防护罩在使用过程中易断裂形成小部件,进而会有引发婴儿窒息的危险。 消费者应当立即停止让儿童使用被召回的安抚奶嘴并将该产品按家庭垃圾分类原则进行处理。
今天出现了一件很惊险的事情,愿意与大家分享:今天和往常一样,把称量瓶放入真空干燥箱内,温度60,开始抽空,突然,听见砰的一声,发现称量瓶的盖子炸了。幸亏有防护罩,不然要出事了
[b]一 [size=16px]厂房与设施管理[/size][/b]1.厂房与设施设置不合理。如:(1)原辅料库未安装通风设施。(2)生产车间中间站未按药品存放要求设置阴凉库。(3)留样样品柜未进行上锁管理。(4)称量间未设置除尘设施。(5)固体制剂车间称量间、压片间等产尘间无防止粉尘扩散的除尘设施。(6)青霉素类粉针车间排出的空气未经过净化处理。(7) 危险品库没有排风通风设施。2.厂房与设施维修保养不到位。如:(1)部分厂房与设施出现损坏、生锈等情况,未及时维修。(2)洁净区对非洁净区、不同级别的洁净区压差不符合规定。(3)固体制剂车间洁净区地面出现破损,表面不平整光滑、存在裂缝。(4)固体制剂车间的墙面、送风口破损、开裂、生锈,未及时维修。(5)生产车间无防蚊虫措施,未定期清理蚊虫尸体并做好记录。(6)生产车间洁净区的地漏未按要求进行液封。[b]二[size=16px]设备管理[/size][/b]3.设备使用管理不规范、或清洁不到位。如:(1)设备清洁后仍有目视可见的污迹。(2)设备使用过程操作人员未及时填写设备使用日志,未对设备使用、清洁、维护和维修情况进行及时记录。(3)生产区内放置的闲置设备在搬离出前无醒目的状态标识。(4)对生产设备需拆洗的关键部件未制定具体且完整的清洁方法。(5)部分生产仪器(如电子天平和电子台秤)未制定使用操作规程。(6)部分生产和检验设备无设备状态标识或清洁状态。(7)小容量注射剂(非终端灭菌)生产前的设备清洁、灭菌情况确认不到位。(8)真空干燥箱已清洁(已挂已清洁标识),现场查看箱内仍有残留水。(9)生产使用的流化床干燥机布袋按品种专用存放,但未对布袋标识进行区分。4.设备的设计、选型、安装不符合预定用途。如:(1)设备的安装不便于生产操作或未按预定用途配备相应的设备。(2)设备不能满足生产工艺要求,生产过程中出现漏液、漏粉,对产品质量可能造成影响。(3)B级洁净区分装机玻璃门生产时未能正常闭合,影响无菌环境保障效果。(4)清洗后瓶子进入隧道烘箱前没有防护罩保护。(5)对照品称量比较小(如称量2mg)的情况下,化验室选用的电子天平(十万分之一)不能满足其称量的精度要求。5.部分设备、仪器未按规定校准,或校准不规范。如:(1)设备、仪器校准的量程范围未涵盖实际生产和检验的使用范围。(2)称量设备不能满足其产品称量的精度要求。(3)洁净区不同区域之间的压差表有校准合格标示,但在无压差情况下压差表未归零。(4)药典筛网校准不规范,缺少筛网网孔径最大偏差和平均丝径两个项目的校准。[img=,290,106]https://ng1.17img.cn/bbsfiles/images/2024/02/202402232145590928_5368_3170710_3.png!w290x106.jpg[/img]
请教各位老师:我们用溶剂(二硫化碳)解析,[url=https://insevent.instrument.com.cn/t/Mp]气相色谱[/url]分析苯系物.但还不知道应该怎样作个人防护措施?分析完后废液该如何处理?二硫化碳用色谱纯或是优级纯好?