德国HYDRO-BIOS公司--Slimline多通道水样采集器
Multi Water Sampler Slimline
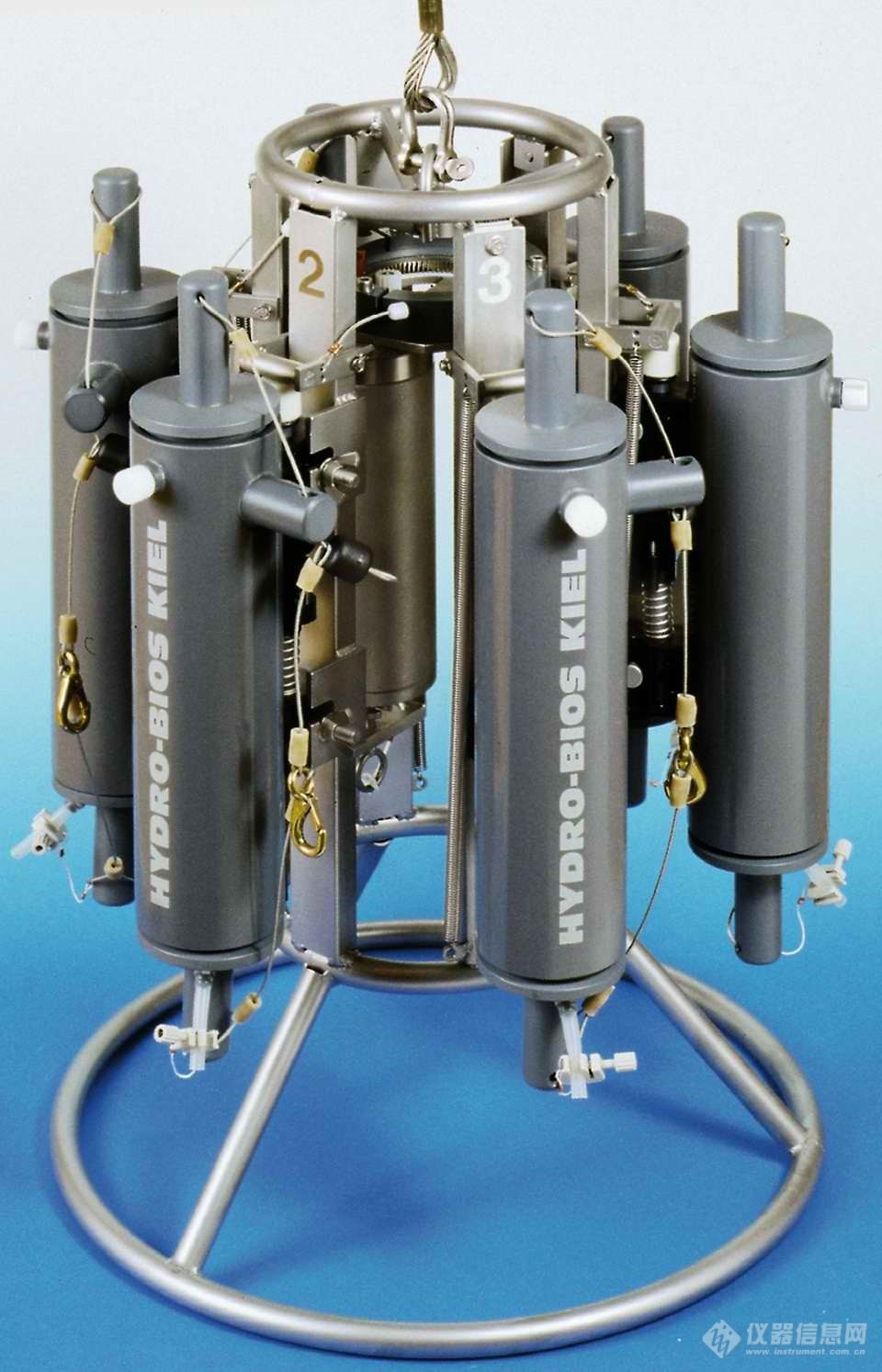

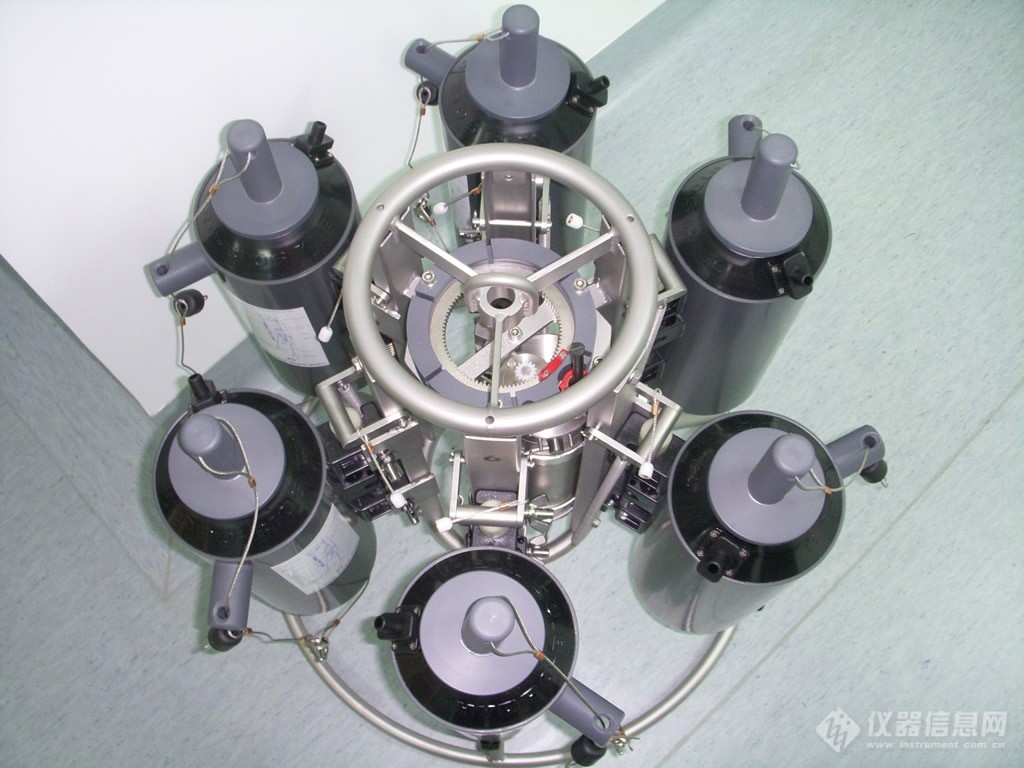
多通道水样采集器Slimline是一款对HYDRO-BIOS MWS 6的改进的轻便型多通道水样采集器,6个采样筒容量为1L、3.5L或5L,具有直径小,质量轻的特点,甚至在小船上也可以很容易地操作。Slimline装有一个马达驱动的自动释放装置,上面集成一个压力传感器,用来测量用户预设的深度。传感器的测量范围可根据用户的工作要求进行选择。Slimline最大工作深度6000米,标准配置3000米。Slimline在工作时电量消耗极少,并且可以在温度为-40℃~+85℃的环境中正常工作。整套系统可以由甲板控制单元上的控制按钮控制,进行在线实时采样;也可按照预先设定的采样深度间隔进行离线自容式采样。
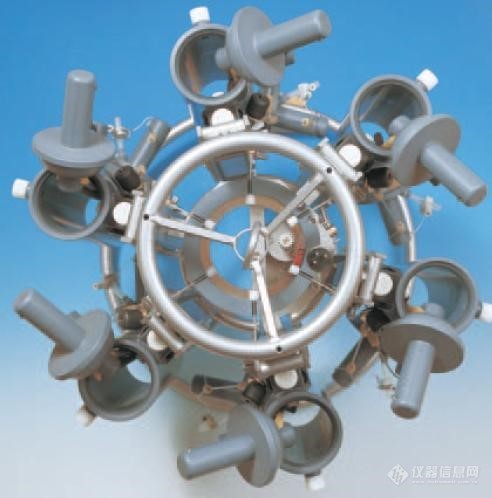


马达单元 Slimline多通道水样采集器俯视结构图
选配件:
- CT-组件:完全整合在多通道水样采集器的驱动单元上,由一个电导率传感器和一个温度传感器组成。
- 各种参数的传感器,如温度、盐度、浊度、叶绿素等
技术参数:
尺寸 | 直径55cm,高度83cm,1L型号
直径65cm,高度88cm,3.5L型号 直径66cm,高度98cm, 5L型号 |
空重 | 约40kg,带6个1L采样器
约45kg,带6个3.5L采样器 约55kg,带6个5L采样器 |
最大操作水深 | 标准配置:3000米;可选配置:6000米 |
阵列 | 不锈钢材质 |
马达单元 | 由钛制成,电池供电(3×DL123A/3V) |
甲板控制单元 | 金属舱室;带一个控制采样器开关的按钮;显示采样筒序号、压力和电池状态带发光二极管背景灯的液晶显示屏;与PC机的接口为RS232;由85-260V交流电或电池 |
压力传感器 | 0.0-3000dbar±0.1%f.s.(标准); |
多通道水样采集器Slimline订购信息:
436 975 多通道水样采集器Slimline
带微处理器和外置电池组的马达驱动单元;
集成压力传感器;16兆数据存储器;
通过PC机控制的可编程式深度依赖性采样间隔;
带甲板控制单元;
配备6个容积为1L的通畅流水样采集器;
436 976 多通道水样采集器Slimline
带微处理器和外置电池组的马达驱动单元;
集成压力传感器;16兆数据存储器;
通过PC机控制的可编程式深度依赖性采样间隔;
带甲板控制单元;
配备6个容积为3.5L的塑料水样采集器;
436 977 多通道水样采集器Slimline
带微处理器和外置电池组的马达驱动单元;
集成压力传感器;16兆数据存储器;
通过PC机控制的可编程式深度依赖性采样间隔;
带甲板控制单元;
配备6个容积为5L的塑料水样采集器;
450 500 CT组件
电导传感器:0~65mS/cm±0.01mS/cm
温度传感器:-2 ~32℃±0.005℃
监测频率:1Hz
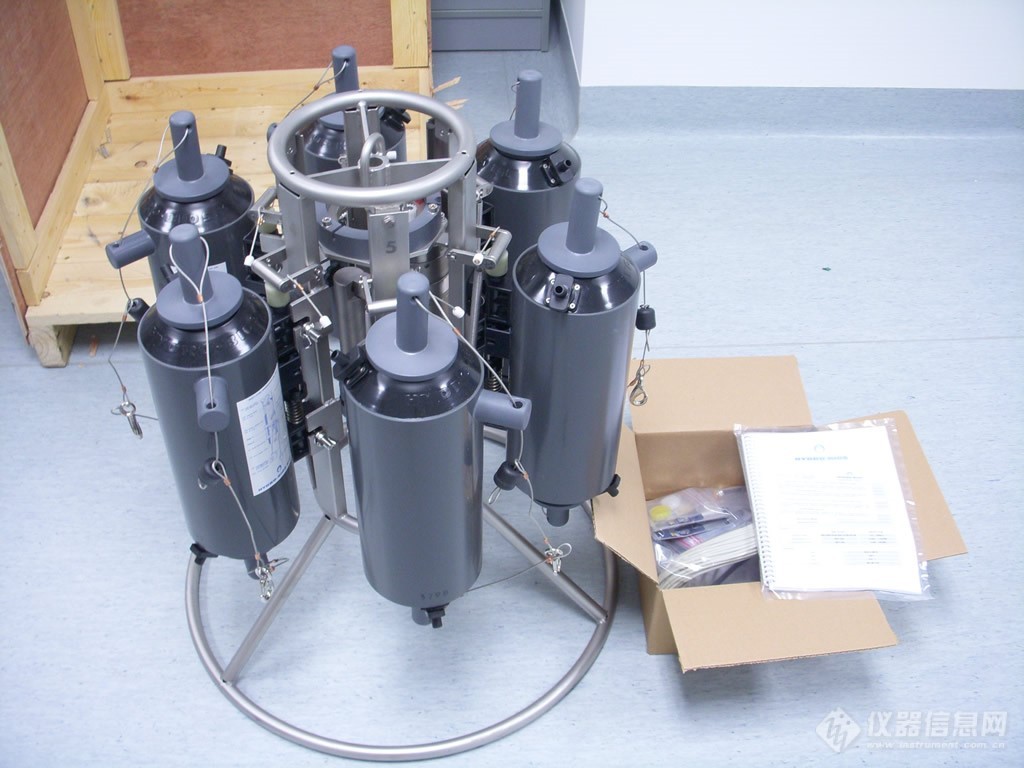
多通道水样采集器Slimline照片集:

| 
|
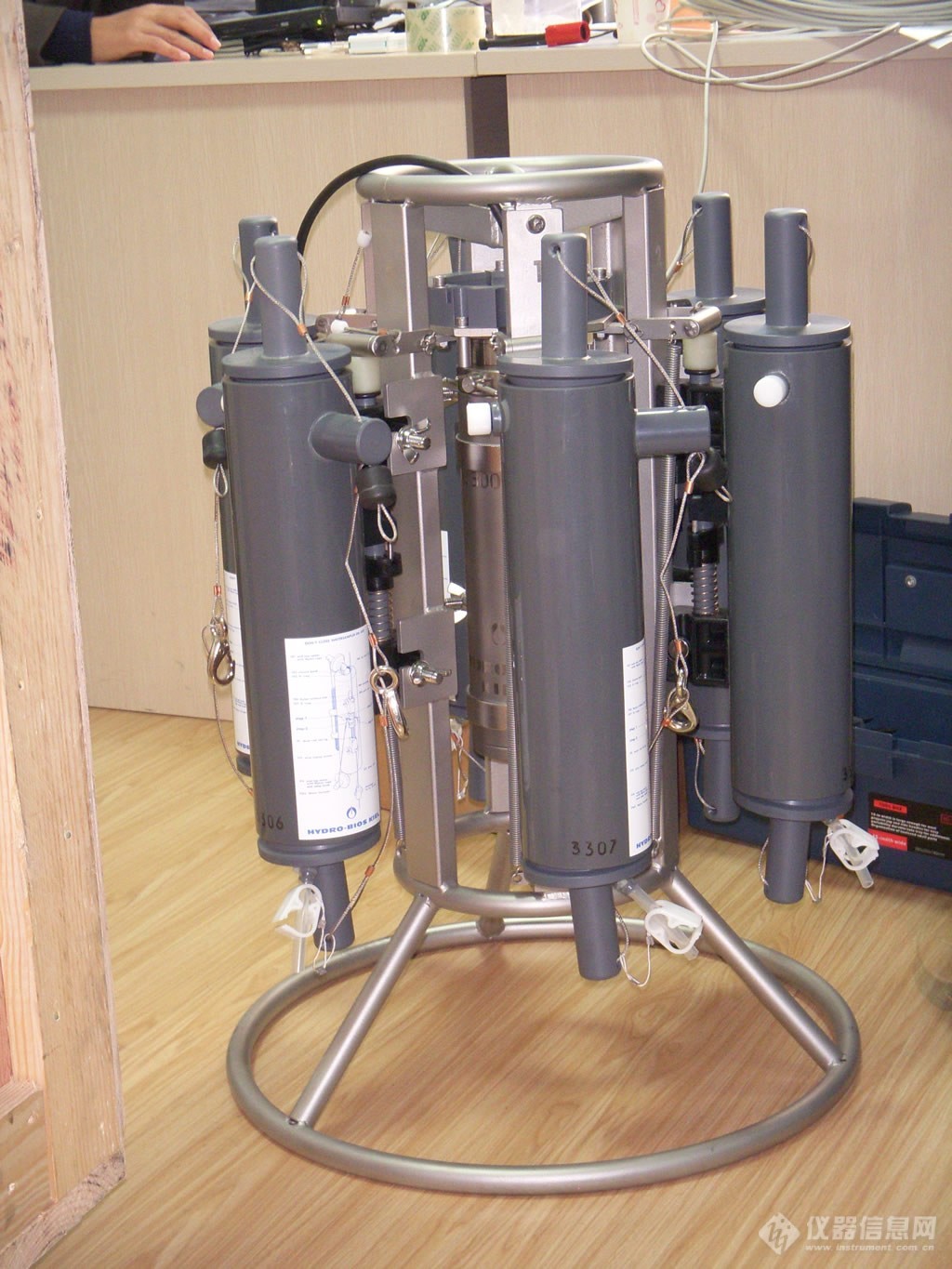
多通道水样采集器Slimline,6X3.5L | 多通道水样采集器Slimline,6X3.5L |
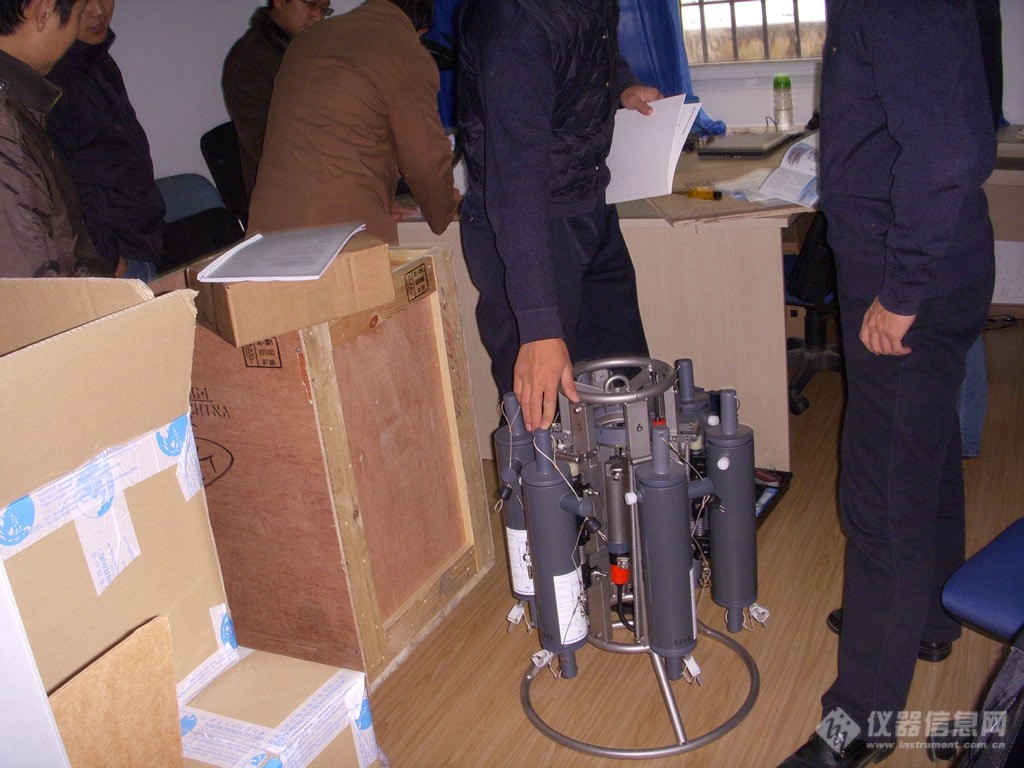

| 
|
用于多通道水样采集器Slimline,6X1L | 多通道水样采集器Slimline,6X1L |

| 
|
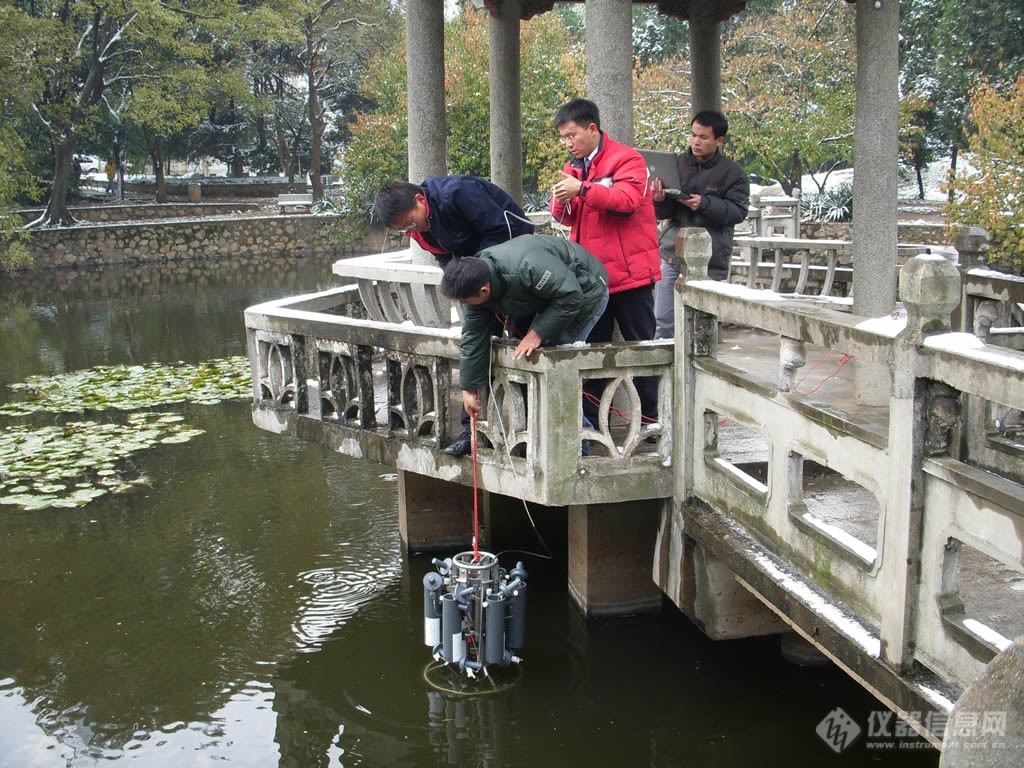
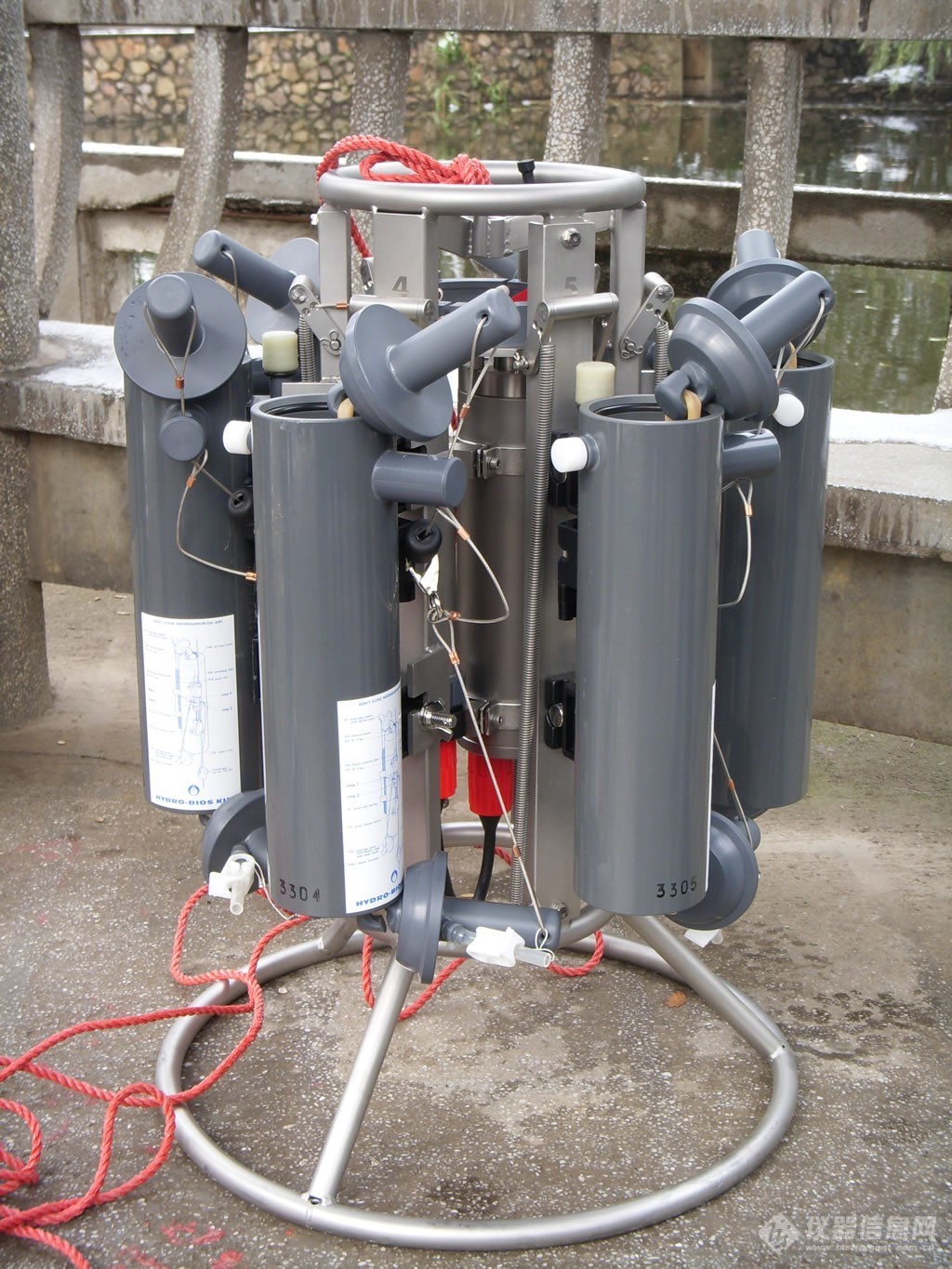
正在采水状态的多通道水样采集器Slimline | 采水前的多通道水样采集器Slimline |
代表文献:
1.Gradinger, Jiirgen Lenz,1989.Picocyanobacteria in the high Arctic.Marine Ecology. Progress series.52:99-101.
2.R. R. Gradinger, M. E. M. Baumann,1991.Distribution of phytoplankton communities in relation to the large-scale hydrographical regime in the Fram Strait.Marine Biology.111(2),311-321.
3.R. J. Gowen, B.M. Stewart, D.K. Mills and P. Elliott,1994.Regional differences in stratification and its effect on phytoplankton production and biomass in the northwestern Irish Sea.Journal of Plankton Research.17(4):753-769.
4.R.J. Gowen, G. McCullough, M. Dickey-Collas and G.S. Kleppel,1997.Copepod abundance in the western Irish Sea: relationship to physical regime, phytoplankton production and standing stock.Journal of Plankton Research.20(2):315-330.
5.K. Richardson, S.H. Jónasdóttir, S.J. Hay, A. Christoffersen,1999.Calanus finmarchicus egg production and food availability in the Faroe–Shetland Channel and northern North Sea: October–March.Fisheries Oceanography.8(1):153–162.
6.M. Trimmer, R. J. Gowen, B. M. Stewart, D. B. Nedwell,1999.The spring bloom and its impact on benthic mineralisation rates in western Irish Sea sediments.Marine Ecology Progress series.185:37-46.
7.Harri T. Kankaanp??, Vesa O. Sipi?, Jorma S. Kuparinen, Jennifer L. Ott, and Wayne W. Carmichael ,1999.Nodularin analyses and toxicity of a Nodularia spumigena (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) water-bloom in the western Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea, in August 1999.Phycologia.40(3):268-274.
8.Andrea M. Sass, Henrik Sass, Marco J. L. Coolen, Heribert Cypionka, and J?rg Overmann,2001.Microbial Communities in the Chemocline of a Hypersaline Deep-Sea Basin (Urania Basin, Mediterranean Sea).Applied and Envioronmental Mcrobiology.67(12):5392-5402.
9.Victor W Truesdale, Günther Nausch, Alex Baker,2001.The distribution of iodine in the Baltic Sea during summer.Marine Chemistry.74(2–3):87–98.
10.Ann K. Manske, Jens Glaeser, Marcel M. M. Kuypers and J?rg Overmann,2005.Physiology and Phylogeny of Green Sulfur Bacteria Forming a Monospecific Phototrophic Assemblage at a Depth of 100 Meters in the Black Sea.Applied and Envioronmental Mcrobiology.71(12):8049-8060.
11.Maik Inthorn, Michiel Rutgers van der Loeff, Matthias Zabel,2006.A study of particle exchange at the sediment–water interface in the Benguela upwelling area based on 234Th/238U disequilibrium.Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers.53(11):1742–1761.
12.Tim J. Waite, Victor W. Truesdale, Jon Olafsson,2006.The distribution of dissolved inorganic iodine in the seas around Iceland.Marine Chemistry.101(1–2):54–67.
13.MAJANEVA Markus, AUTIO Riitta, HUTTUNEN Maija, KUOSA Harri, KUPARINEN Jorma,2009.Phytoplankton monitoring: the effect of sampling methods used during different stratification and bloom conditions in the Baltic Sea.Boreal environment research.14(2):313-322.
14.Bertics, Victoria J., L?scher, C. R., Salonen, I., Dale, Andy W., Gier, Jessica, Schmitz, R.A. and Treude, Tina,2013.Occurrence of benthic microbial nitrogen fixation coupled to sulfate reduction in the seasonally hypoxic Eckernf?rde Bay, Baltic Sea.Biogeosciences(BG).10(3):1243-1258.
15.W. DAVISON,1977.Sampling and handling procedures for the polarographic measurement of oxygen in hypolimnetic waters.Freshwater Biology.7(4):393–401.
16.Austin B. M. Egbore,1978.Seasonal variations in the density of a small West African lake.Hydrobiologia.61(3):195-203.
17.Dr. U. Zaiss, P. Winter, H. Kaltwasser,1982.Microbial methane oxidation in the River Saar.Journal of Basic Microbiology.22(2):139–148.
18.V.F. Samanidou & I.N. Papadoyannis,1992.Study of heavy metal pollution in the waters of Axios and Aliakmon rivers in northern Greece.Journal of Environmental Science and Health . Part A: Environmental Science and Engineering and Toxicology.27(3):587-601.
19.Nilgün Kazanci, Reiner-Hartmut Plasa, Eike Neubert & Afife ?zbirak,1992.On the limnology of Lake K?ycegiz (SW Anatolia).Zoology in the Middle East.6(1):109-126.
20.Eduardo González-Mazo, Jesus María Forja, Abelardo Gómez-Parra ,1998.Fate and Distribution of Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonates in the Littoral Environment.Environ. Sci. Technol..32(11):1636–1641.
21.V.M León, E González-Mazo, A Gómez-Parra,2000.Handling of marine and estuarine samples for the determination of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates and sulfophenylcarboxylic acids.Journal of Chromatography A.889(1-2):211–219.
22.Claus-Peter Stelzer,2001.RESOURCE LIMITATION AND REPRODUCTIVE EFFORT IN A PLANKTONIC ROTIFER.Ecology.82(9):2521–2533.
23.Udo Noack, Thomas Geffke, Ramani Balasubramanian, Jutta Papenbrock, Mike Braune, Dirk Scheerbaum,2004.Effects of the Herbicide Metazachlor on Phytoplankton and Periphyton Communities in Outdoor Mesocosms.Acta hydrochimica et hydrobiologica.31(6):482–490.
24.L. R. Rodríguez-Gallego, N. Mazzeo, J. Gorga, M. Meerhoff, J. Clemente, C. Kruk, F. Scasso, G. Lacerot, J. García, F. Quintans,2004.The effects of an artificial wetland dominated by free-floating plants on the restoration of a subtropical, hypertrophic lake.Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management.9(3-4):203–215.
25.Kristina Samuelsson, Johnny Berglund, and Agneta Andersson,2006.Factors structuring the heterotrophic flagellate and ciliate community along a brackish water primary production gradient.Journal of Plankton Research.28(4):345-359.
26.George Kehayias, Ekaterini Chalkia, Stavroula Chalkia, George Nistikakis, Ierotheos Zacharias, Anastasios Zotos,2008.Zooplankton dynamics in the upstream part of Stratos reservoir (Greece).Biologia.63(5):699-710.
27.MAJANEVA Markus, AUTIO Riitta, HUTTUNEN Maija, KUOSA Harri, KUPARINEN Jorma,2009.Phytoplankton monitoring: the effect of sampling methods used during different stratification and bloom conditions in the Baltic Sea.Boreal environment research.14(2):313-322.
![]()
![]()