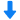
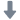
湍动槽中耗散元素检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A new method to describe small scale statistical information from passive scalar fields has been
proposed by Wang and Peters (2006). They used direct numerical simulations (DNS) of homogeneous shear
flow to introduce the innovative concept. This novel method determines the local minimum and maximum
points of a fluctuating scalar field via gradient trajectories starting from every grid point in the direction of
the steepest ascending and descending scalar gradients. Relying on gradient trajectories, a dissipation element
is defined as the region of all the grid points the trajectories of which share the same pair of maximum
and minimum points. The procedure has also been successfully applied to various DNS fields of homogeneous
shear turbulence using the three velocity components and the kinetic energy as scalar fields. To validate
statistical properties of these elements derived from DNS (Wang and Peters 2006, 2008), dissipation elements
are for the first time determined based on experimental data of a fully developed turbulent channel
flow. The dissipation elements are deduced from the gradients of the instantaneous fluctuation of the three
velocity components u5, v5, and w5 and the instantaneous kinetic energy k5, respectively. The required 3D velocity
data is obtained investigating a 17.82 × 17.82 × 2.7 mm3 (0.356 × 0.356 × 0.054 ) test volume
using tomographic particle-image velocimetry (Tomo-PIV). The measurements are conducted at a Reynolds
number of 1.7× 104 based on the channel half-height and the bulk velocity U. Detection and analysis of
dissipation elements from the experimental velocity data are presented. The statistical results are compared
to the DNS data from Wang and Peters (2006, 2008).
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
耗散元素
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
铁-金核壳纳米粒子中相位结构检测方案(激光产品)
The influence of the pulse duration was investigated using a picosecond pulsed laser (Atlantic 532, Ekspla) with a wavelength of 1064 nm, a pulse duration of 10 ps, a pulse energy of 160 μJ, a repetition rate of 100 kHz, and a focal distance of 100 mm.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
相位结构
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流体中速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The unsteady pressure field is obtained from time-resolved tomographic particle image
velocimetry (Tomo-PIV) measurement within a fully developed turbulent boundary layer at free stream
velocity of U∞ = 9.3 m/s and Reθ = 2400. The pressure field is evaluated from the velocity fields
measured by Tomo-PIV at 10 kHz invoking the momentum equation for unsteady incompressible flows.
The spatial integration of the pressure gradient is conducted by solving the Poisson pressure equation with
fixed boundary conditions at the outer edge of the boundary layer. The PIV-based evaluation of the
pressure field is validated against simultaneous surface pressure measurement using calibrated condenser
microphones mounted behind a pinhole orifice. The comparison shows agreement between the two
pressure signals obtained from the Tomo-PIV and the microphones with a cross-correlation coefficient of 0.6
while their power spectral densities (PSD) overlap up to 3 kHz. The use of the Tomo-PIV system with the
application of three-dimensional momentum equation shows higher accuracy compared to the planar version
of the technique. The combination of a correlation-sliding-average technique, the Lagrangian approach to
the evaluation of the material derivative and the planar integration of the Poisson pressure equation results in
the best agreement with the pressure measurement of the surface microphones.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
粒子成像测速技术中复杂等离子体检测方案
• PIV is a fluid measurement technique that is used to determine the average displacement of a group of particles.
• PIV offers advantages over particle tracking by enabling the rapid reconstruction of spatially resolved two-and three-dimensional
velocity fields.
• PIV has facilitated detailed measurements of a wide variety of phenomena in complex (dusty) plasmas from particle transport to
DAW/DDW to thermal properties.
• New developments:
o Detailed benchmarking of PIV against simulations
o Spatially resolved stereo-PIV
o Tomographic PIV
o Time-resolved PIV
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
复杂等离子体
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
水流,空化,气泡中速度场,雷诺应力,应力张量检测方案
The purpose of this experimental study was to analyze a 2D
cavitating shear layer. The global aim of this work was a better
understanding and modeling of cavitation phenomena from a
2D turbulent shear flow to rocket engine turbopomp inducers.
This 2D mixing layer flow provided us a well documented
test case to be used for comparison between the behavior with
and without cavitation. Similarities and differences led to
characterize effects of the cavitation on the flow dynamic.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,雷诺应力,应力张量
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
反向旋转盘片中剪切层不稳定性的实验和数值模拟研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The shear layer instability in the flow between two counter-rotating disks enclosed by
a cylinder is investigated experimentally and numerically, for radius-to-height ratio
Γ =R/h between 2 and 21. For sufficiently large rotation ratio, the internal shear layer
that separates two regions of opposite azimuthal velocities is prone to an azimuthal
symmetry breaking, which is investigated experimentally by means of visualization
and particle image velocimetry. The associated pattern is a combination of a sharpcornered
polygonal pattern, as observed by Lopez et al. (2002) for low aspect ratio,
surrounded by a set of spiral arms, first described by Gauthier et al. (2002) for high
aspect ratio. The spiral arms result from the interaction of the shear layer instability
with the Ekman boundary layer over the faster rotating disk. Stability curves and
critical modes are experimentally measured for the whole range of aspect ratios, and
are found to compare well with numerical simulations of the three-dimensional timedependent
Navier–Stokes equations over an extensive range of parameters. Measurements
of a local Reynolds number based on the shear layer thickness confirm that a
shear layer instability, with only weak curvature effect, is responsible for the observed
patterns. This scenario is supported by the observed onset modes, which scale as the
shear layer radius, and by the measured phase velocities.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
剪切层不稳定性的实验和数值模拟研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流风机中扩散放大器性能的实验研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The performance of a vertical axis wind turbine with and without a diffuser was studied
using direct force measurement technique applied to a scaled model of the rotor in a
water tunnel. The experiment was conducted at different tip-speed ratios. The maximum
power coefficient for the turbine was found to be equal to 0.35 for the rotor with diffuser
and to 0.26 for the rotor without diffuser. Therefore, the maximum power coefficient was
increased by 35% when the diffuser was used in the configuration.
In the second part of this work, the flow patterns downstream of the turbine were
studied by the particle image velocimetry (PIV) technique. Six different tip-speed ratios
were considered for each configuration (with and without a diffuser). The vorticity and
the streamline plots provide insight into the flow physics in each configuration. In
addition, the swept area of a full-scale rotor was calculated for both a diffuser-augmented
and a bare turbine for a range of power outputs.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
扩散放大器性能的实验研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
空化混合层中速度场分析检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The purpose of this experimental study was to analyze a two-dimensional cavitating shear layer.
The global aim of this work was to improve understanding and modeling of cavitation
phenomena, from a 2D turbulent shear flow to rocket engine turbopomp inducers. This 2D mixing
layer flow provided us with a well documented test case to be used for comparisons between
behavior with and without cavitation. Similarities and differences enabled us to characterize the
effects of cavitation on flow dynamics. The experimental facility enabled us to set up a mixing
layer configuration with different cavitation levels. The development of a velocity gradient was
observed inside a liquid water flow using PIV–LIF (particle image velocimetry–laser induced
fluorescence). Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities developed at the interface and vaporizations and
implosions of cavitating structures inside the vortices were observed. The mixing area grew
linearly, showing a constant growth rate, for the range of cavitation levels studied. The spatial
development of the mixing area seemed hardly to be affected by cavitation. Particularly, the
self-similar behavior of the mean flow was preserved despite the presence of the vapor phase.
Successive vaporizations and condensations of the fluid particles inside the turbulent area
generated additional velocity fluctuations due to the strong density changes. Moreover, when
cavitation developed, the Kelvin-Helmholtz vortex shape was modified, inducing a strong
anisotropy (vortex distortion as ellipsoidal form) due to the vapor phase. The main results of this
study clearly showed that the turbulence-cavitation relationship inside a mixing layer was not
simply a change of compressibility properties of the fluid in the turbulent field, but a mutual
interaction between large and small scales of the flow due to the presence of a two-phase flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场分析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
环形喷嘴中利用声激发主动控制大直径比初始区域环形不稳定性检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (P.O.D.) is a technique used for analysis of vortex structures in a turbulent flow. In this study, complex shear flows are observed by P.I.V. measurements (Particle Image Velocimetry) of a large diameter ratio annular jet. The annular jet is an example of complex shear flow situations. Two axisymmetric shear layers, originating at the jet exit, one at the nozzle lip and the other at the centre body, eventually meet downstream or interact with each other. The main aim of this study is to observe and analyze the effects of active control using acoustic waves on an annular jet with a great diameter ratio (r= 0.91), in order to find a new way to reduce jet instabilities. This contribution discusses the application of Proper Orthogonal Decomposition to the P.I.V. (Particle Image Velocimetry) velocity fields of an annular jet and on a statistic of time resolved tomographic images of the initial zone of the annular jet. Acoustic waves are then applied on the annular jet with different frequencies (fundamental, first harmonic̷). Measurements are conducted with a Reynolds number ReDo=107800. The fluctuation frequency of the stagnation point is known for this Reynolds number. The Strouhal number corresponding to this frequency is StDo = 0.27. The P.O.D. analysis applied on a natural annular jet and an excited annular jet enables us to see the importance of the triggering of the acoustic wave with the stagnation point motion. An active control is therefore necessary to use acoustic excitation to reduce instabilities in the initial zone of these turbulent jets. Active control has already been used with round jets and has given promising results, but only a few studies have been conducted on annular jets in this field. This work will permit us essentially to have a better knowledge of annular jets and to meet manufacturers' needs.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
利用声激发主动控制大直径比初始区域环形不稳定性
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
水流中实验流体力学和计算流体力学的研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A complementary experimental and computational study of plunging breaking waves is presented that are generated in
a two dimensional open channel flume using a bottom bump and impulsive accelerated flow. The time evolution of the transient
wave and its flow properties are measured using experimental fluid dynamics (EFD): upstream and downstream velocity
and flow rates using pitot probes; air-water interface elevation measurements and two dimensional particle image velocimetry
in the wave breaking region. The computational fluid dynamics (CFD) methods are: Cartesian grid; embedded-
boundary; hybrid HSM/GF/particle level set and VOF methods, and LES. CFD wave profiles at various time steps
identifies the overall wave breaking process and major events: max wave height, first plunge, oblique splash-up, vertical jet,
air entrainment, two repeats of these processes, dissipation and wave swept downstream which is qualitatively validated by
EFD results. Both EFD and CFD results showed two subsequent plunging and splash-up events after the first plunge. After
the wave breaks, the flow trends in mean velocity and vorticity observed in EFD are very similar to CFD which has more
detailed resolutions of plunging, splashing, vertical jet and bubble entrainment. Current studies also revealed the occurrence
of chaotic multiple splash-up events after the third plunging that produce span-wise vorticity and turbulence. Generation of
a clockwise rotating bump vortex and an anticlockwise rotating span-wise wave breaking vortex that is created from the
entrapped air after the breaking which transports turbulence from the trough towards the bulk fluid, were identified as the
two important events. Mean values of turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) below the broken wave showed that the TKE levels
increase by almost 90% after the first plunge and another 40% after the second plunge, after which as the wave is swept
downstream by the accelerating mean flow the TKE dissipates.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
实验流体力学和计算流体力学的研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
台阶中多台阶通道中的爆震衍射检测方案(粒子图像测速)
This research investigated multiple detonation diffraction events in order to better
understand the limits and benefits of diffraction strategies with respect to pulse
detonation engine design. Hydrogen/air detonations were generated using swept
ramp obstacles in a 1.27 m long channel with a cross section of 25.4 mm by 88.9
mm and were diffracted into various multiple-stepped openings. This allowed the
detonation wave diffraction transmission limits to be determined for hydrogen/air
mixtures and to better understand reinitiating mechanisms throughout the
diffraction process. Tests were conducted for area ratios ranging from 2.00–2.60
with varying equivalence ratios from 0.5–1.5.
Computational methods were used to better understand the diffraction
phenomenon using a series of sensitivity studies for different chemistry sets,
computational cell size and equivalence ratio. Experimental tests used combined
optical shadowgraph and particle image velocimetry imaging systems to provide
shock wave detail and velocity information. The images were observed through
a newly designed explosive proof optical section and split flow detonation
channel. It was found that area ratios of 2.0 could survive single and double
diffraction events over a range an equivalence ratio range of 0.8 to 1.14 Area
ratios of 2.3 survived the primary diffraction event for equivalence ratios near
stoichiometric for the given step length. Detonation diffraction for area ratios of
2.6 did not survive the primary diffraction event for any equivalence ratio and
were unable to transmit to a larger combustor.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
多台阶通道中的爆震衍射
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
搅拌槽中流体力学和喷射注入研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
To quench a thermal runaway reaction in a chemical rector, an efficient approach is the introduction of a small quantity of a liquid inhibiting agent, named a “killer”, into the mixing
vessel. In this thesis, an experimental approach has been coupled tightly with numerical modelling using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). The first part of this thesis is devoted to a study of the hydrodynamics of partially-baffled mixing vessels, including the free-surface deformation caused by the central vortex. The use of an inhomogeneous, multiphase approach allowed simulation of the free-surface deformation. The capability of this novel method was
demonstrated by very good agreement between the numerical predictions and experimental data. In the second part, liquid jet injection at the free-surface was coupled with the vessel hydrodynamics. Numerical results, obtained using an Eulerian-Lagrangian approach, have again shown good agreement with experimental data. These results allowed the jet trajectory to be modelled and its penetration into the agitated vessel was quantified. New mixing criteria were introduced that are specific to this application. Finally, the numerical methods validated at the pilot scale were applied at the industrial scale and allowed the proposal of practical improvements to the safety of the synthesis reactors studied.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流体力学和喷射注入研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
水流中湍流中进行拉格朗日加速度测量检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Acceleration is of primal relevance in fluid mechanics, as it shows the effect of the combination of all the forces acting on a fluid flow; the Navier-Stokes equations highlight this fact and the importance of its knowledge in the description of a fluid motion:
Moreover, only in few particular cases (as for example, in parallel fluxes such as Couette one) it is possible to analytically solve them: for the other cases it would be important to measure their single components. Unfortunately, despite the acceleration is at
the very base of fluid motion (see, for instance, Tsinober 2001), only few measurement of the acceleration in the Lagrangian frame can be found in literature. Even if, on one hand, a certain number of authors have studied acceleration properties via numerical simulations, for instance Vedula and Yeung (1999), Tsinober et al. (2001), Biferale et al. (2004), Goto et al. (2005), Osborne et al. (2005), Chen et al. (2006), on the other very few examples of its experimental measure are available up to now. Moreover,among them not all the measurements are taken in the Lagrangian frame: among the
Eulerian measurements, Christensen and Adrian (2002), Dong et al. (2001) and Lowe and Simpson (2005) can be pointed out, among the Lagrangian ones, Virant and Dracos (1997), Ott and Mann (2000), La Porta et al. (2001), Voth et al. (2002) and Luthi et al.(2005) can be found.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
湍流中进行拉格朗日加速度测量
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
PIV测量技术中性能优势检测方案
Active flow control earns growing interest for manufacturers of large transport aircraft
because of the constant need to improve these aircraft in terms of less fuel consumption,
higher efficiency, steep approaches and departures and less weight. Flow control devices
that are based on fluidic actuators, e.g. vortex generator jets (VGJs), have shown a promising
potential to influence separating boundary layers and keep them attached (e.g. Godard &
Stanislas (2006a‐c); Johari. & Rixon (2003); Johnston & Nishi (1990); Mc Manus et al. (1996);
Ortmanns et al. (2008a); Pauley & Eaton (1988); Scholz et al. (2006)). For an efficient operation
such devices need to be optimized regarding their ability to influence the flow. However,
optimization turns out to be very challenging because of the vast parameter space and the
lack of an adequate “figure of merit”. The proposed contribution will discuss the possibility
to assess and optimize such devices by analyzing the velocity fields from stereoscopic PIV
measurements.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
性能优势
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
电容中耦合射频放电的电子加热检测方案(CCD相机)
Electron heating, mechanisms of plasma generation, and electron dynamics in dif-
ferent types of capacitively coupled radio frequency (CCRF) discharges relevant for
industrial applications are investigated by a combination of di®erent experimen-
tal diagnostics, simulations and models. Geometrically symmetric and asymmetric
single frequency discharges operated at low pressures, geometrically symmetric dual
frequency discharges operated at two substantially di®erent frequencies and two sim-
ilar frequencies (fundamental and second harmonic with variable phase shift between
the driving voltages) as well as hybrid capacitively/inductively coupled (CCP-ICP)
RF discharges are studied. Electron heating is found to be strongly a®ected by
phenomena characteristic for a certain discharge type, that do not occur in another.
At low pressures the generation of highly energetic electron beams by the expand-
ing sheath is observed. Such beams propagate through the entire plasma bulk and
are re°ected at the opposing plasma boundaries, if the electron mean free path is
long enough. An analytical model demonstrates that these beams lead to an en-
hanced high energy tail of the electron energy distribution function and are, there-
fore, closely related to stochastic heating
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
耦合射频放电的电子加热
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
水流中流体成像分析和描述检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In the Fluid project, WorkPackage 1 is devoted to the creation of an image sequence
database with controlled 2D/3D experimental and numerical
ow
elds. The objective of
this workpackage is to produce complete sets of data comprising:
meteorological satellite atmospheric image sequences;
rst sets of image sequences of controlled
uid mechanics experiments (air
ows in
wind tunnels), produced in a classical way using laser-sheets and cameras, with a
smoke or particle concentration chosen a priori in order to give reasonably detectable
contrasts;
second sets of experimental image sequences produced in an adapted manner (seeding,
lighting, frame size, physical data range) after feedback from tests conducted
in WP 2, WP 3 and WP 4;
synthetic image sequences coming from the results of Direct Numerical Simulations
(DNS) of shear
ows;
quantitative data characterising the
ows corresponding to each set of experimental
image sequences, among which global and local physical characteristics like velocity
elds, statistics, spatial correlation as well as topological dimensions of speci
c
regions of the
ow (formation length, layer thickness, virtual origins, wave length,
etc).
This report is the deliverable D1.23 on the production and di
usion of
uid mechanics
images and data. All the dataset distributed during the
rst year to the di
erent partners
are described. Section 2 concerns two experimental datasets, the
rst one is not time
resolved but the second is. Section 3 presents 2D-synthetic data of analytic
ows, DNS
of 2D sustained turbulent
ow and a sample of 2D
ow from PIV Challenge. The last
section 4 is devoted to 3D-synthetic data.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流体成像分析和描述
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
粒子成像测速系统的数据分析中粒子成像测速系统的数据分析检测方案
The emission of oxides of nitrogen, or NOx, by aircraft is an international concern. NOxcontributes to smog in the lower atmosphere and destroys ozone in the stratosphere. To reduce NOxand other harmful emissions, NASA has developed Multipoint Lean-Direct Injection (MP-LDI). To determine the effectiveness of MP-LDI and its potential for future commercial use, particle image velocimetry (PIV) obtains velocity data which is important for setting the inlet and boundary conditions needed for validating computational fluid dynamics codes such as the National Combustor Code (NCC).
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
粒子成像测速系统的数据分析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
鱼道中2D非稳定流动实验研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Vertical slot fish passes have been applied as a solution to mitigate fish migration problems in running waters, for over
two decades. They are commonly used to enable target fish to ascend through obstacles in rivers. However, small
species are rarely considered in such fishways, of which the performance for small fish still remains unknown. This
experiment was to study the turbulence structure in a vertical slot fish pass concerning two different pool length/width
ratios of 9 and 6.67 as well as the effect of installing a cylinder behind the slot in affecting the characteristics of
instationary flow. Cylinders are considered an effective solution to modify the flow structure and to reduce velocity and
turbulent energy in order to adapt the flow for the passage of small fish species. Flow visualization and particle image
velocimetry were used to study the characteristics of mean flow and turbulence and particular emphasis on the unsteady
flow. The results show that flow patterns consist of a water jet and one or two recirculation zones depending on the
length/width ratio of the pool. The direction of the jet was strongly affected by the vertical cylinders. The frequencies
and spatio-temporal evolutions of the main jet beats were analyzed. Combining with the previous studies of fish
migration experiments, the results provide hydraulic evidence on the biological performance.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
2D非稳定流动实验研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
流化床中碰撞特性对喷动流化床动力学影响的实验研究检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In this paper we experimentally study the effect of collision properties of
different particle systems on the bed dynamics of a spout fluidized bed. This
is done for different flow regimes: the spout-fluidization regime (case A), the
jet-in-fluidized-bed regime (case B) and the spouting-with-aeration regime
(case C). The considered particle systems comprise glass beads,
-alumina
oxide and zeolite 4A particles, which are all classified as Geldart D. A nonintrusive
measurement technique is used, viz. particle image velocimetry
(PIV) to measure the particle flow field in a pseudo two-dimensional (2D)
spout fluidized bed. Additionally, digital images are analyzed using a newly
developed digital image analysis (DIA) algorithm to evaluate the particle
volume fraction. It is demonstrated that the new proposed DIA algorithm
provides reliable information on the particle volume fraction distribution,
showing that it is a powerful tool when combined with PIV. The added value
of DIA is confirmed by comparing the particle velocity fields and volumetric
particle fluxes. The effect of the collision properties for glass beads,
-
alumina oxide and zeolite 4A particles has been studied in three flow regimes,
i.e. the intermediate/spout-fluidization regime (case A), the jet-in-fluidizedbed
regime (case B) and the spouting-with-aeration regime (case C). For each flow regime, the particle volume fraction shows small differences between
the different particle systems. For the
-alumina oxide and zeolite 4A
particles, the spout channel is less stable for the cases A and C. The particle
fluxes display also small differences between the particle systems for each
flow regime.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
碰撞特性对喷动流化床动力学影响的实验研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
空气流体中速度矢量场,噪声检测方案
In this paper, we study the acoustic emissions
of the flow over a rectangular cavity. Especially, we
investigate the possibility of estimating the acoustic
emission by analysis of PIV data. Such a possibility is
appealing, since it would allow to directly relate the flow
behavior to the aerodynamic noise production. This will
help considerably in understanding the noise production
mechanisms and to investigate the possible ways of
reducing it. In this study, we consider an open cavity with
an aspect ratio between its length and depth of 2 at a
Reynolds number of 2.4 9 104 and 3.0 9 104 based on the
cavity length. The study is carried out combining high
speed two-dimensional PIV, wall pressure measurements
and sound measurements. The pressure field is computed
from the PIV data. Curle’s analogy is applied to obtain the
acoustic pressure field. The pressure measurements on the
wall of the cavity and the sound measurements are then
used to validate the results obtained from PIV and check
the range of validity of this approach. This study demonstrated
that the technique is able to quantify the acoustic
emissions from the cavity and is promising especially for
capturing the tonal components on the sound emission.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场,噪声
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
离子体中制动器控制高升力翼型下弯襟翼的流动分离检测方案(粒子图像测速)
In current wing design, multiple flaps are incorporated into the trailing edge to allow mixing of
high and low pressure sides to reduce flow separation. These flaps reduce the efficiency by
adding weight and complexity to the aircraft. A single hinged flap would reduce these
inefficiencies but is more susceptible to flow separation. Active flow control is a means by
which the fluid flow over a body is deliberately altered and can be altered such that it becomes
less likely to separate from the object. By energizing the flow, the degree of separation of the
flow can be controlled, and this inherently controls lift. Dielectric barrier discharge (DBD)
plasma actuators are a form of active flow control. These actuators are created by
asymmetrically aligning two electrodes and adding a dielectric layer between the electrodes.
When the electrodes are electrically connected, ionized air (plasma) travels from the exposed
electrode towards the covered electrode. Collisions occur between the plasma and neutral air
over the body, and momentum is transferred to the neutral air, effectively energizing it. The
purpose of this study is to examine the lift enhancement and flow control authority that multiple
DBD plasma actuators have on a high-lift airfoil when compared to the flow exhibited by noncontrolled
and single DBD plasma actuator controlled cases. Electrodes were mounted onto a
simplified NASA Energy Efficient Transport airfoil near the flap. The airfoil was tested in a
closed, recirculating wind tunnel operating at a Reynolds number of 240,000, 20° flap deflection
angle and 0° degree angle of incidence. The actuators were independently powered in order to
determine the most effective input parameters. Using multiple actuators operated in-phase has
increased the lift and has delayed flow separation on the trailing edge flap when compared to
baseline and single actuation cases.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
制动器控制高升力翼型下弯襟翼的流动分离
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2271篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等