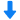
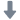
碳烟,火焰,流体中速度场,浓度场,碳烟体积分数,碳烟初级粒径检测方案(粒子图像测速)
An experimental study of the interaction of a planar diffusion flame with a line vortex is presented. A planar
diffusion flame is established between two coflowing, equal velocity streams of acetylene diluted with nitrogen
and air. A line vortex is generated on demand by momentarily pulsing one of the flow streams by way of electromagnetic
actuation of a piston in the flow apparatus. The flame–vortex interactions are diagnosed by planar
laser-induced incandescence for soot yield and by particle image velocimetry for vortex flow characterization. The
results show that soot formation and distribution are influenced by the reactant streams from which vortices are
initiated. The vortices interacting with the flame from the air side produce more soot and soot is distributed in and
around the vortex core in diffuse layers. In contrast, topography of soot in vortices interacting from the fuel side
is such that soot is confined to thinner layers around the vortex core which does not contain any soot. The flame
curvature is found to influence the local soot production with the flame regions convex to the fuel side containing
more soot locally. It is also found that the overall soot yield is less sensitive to the vortex strength and is of lower
magnitude when vortex is spun from the fuel side. The knowledge of this type of asymmetry in soot yield in
flame–vortex interactions is useful for combustion engineering and design of practical devices.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,浓度场,碳烟体积分数,碳烟初级粒径
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
微型驱动马达,同轴喷嘴,流向漩涡中流向漩涡演化研究,速度场,速度矢量场,漩涡结构,涡结构检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A coaxial jet was actively controlled by a MEMS-fabricated micro flap actuator nozzle. The effect of
different control modes on secondary azimuthal instabilities and the evolution of streamwise vortices
were investigated by applying stereoscopic PIV to the cross-stream plane of the jet. Forcing with
non-symmetric modes, in particular the least-stable helical mode, accelerates the evolution of the
streamwise vortices through the enhancement of azimuthal instabilities. Although forcing is applied
to the outer shear layer of the outer jet, the control effect is most pronounced in the inner shear layer
of the inner jet. Unlike in the natural jet, streamwise vortices appear in the inner shear layer of the
controlled jet. For forcing with the fundamental axisymmetric mode, a Strouhal number of the order
of unity maximise the azimuthal instabilities and hence the counts of the streamwise vortices. The
present result is in accordance with our previous experimental findings in the longitudinal plane,
where the evolution of the primary vortices and mixing between the inner and the outer jets were
examined through 2D-PIV and PLIF (Kurimoto et al., 2004, Active control of coaxial jet mixing with
arrayed micro actuators. Transactions of the Japanese Society of Mechanical Engineers, pp. 31–38.)
This emphasises the connection between primary and streamwise vortices and their significance in the
mixing enhancement process. It is also found that the azimuthal wavelength under the present control
scheme is almost the same as that of the natural jet and independent of the streamwise position.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流向漩涡演化研究,速度场,速度矢量场,漩涡结构,涡结构
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
微流动装置中速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Along with the rapid growth of research of microfluidics, monitoring and understanding micro flow
behavior is a challenge for researchers. Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV), a powerful tool that
makes flow visible, was extended to microscale by Santiago et al. 1998. In this paper, we presented
the micro Particle Image Velocimetry (μPIV) system at Nanyang Technological University (NTU),
its calibration and characterizations of microfluidic devices using μPIV. Since the fully developed
microchannel flow has been well investigated, it is suitable to calibrate the measurements of μPIV.
In our experiment, an in-channel microdispenser fabricated on printed circuit board is used to form a
microchannel. A syringe pump forces water that contains fluorescent particles. The flow field is obtained
by μPIV. At the same time, a three-dimensional model with ANSYS/FLOTRAN was used.
The comparison between the two results demonstrates that our μPIV system works well. Furthermore
we use this system to characterize a Tesla valve - a non-moving part valve. The valve consists
of a fluid channel structure that has rectification property, which favors forward flow while hampers
reverse flow. The velocity fields are also validated by ANSYS/FLOTRAN.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
喷雾,液滴,喷嘴,流体中速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Pulsed jets have found a wide variety of applications in the area of flow control during
the recent years. The goal of the current study is to identify the flow field and mixing
characteristics associated with an incompressible circular jet through a flexible nozzle. The
flow was self-excited over a range of conditions and produced a pulsatile flow. The frequency
of excitation was found to be between 150-175Hz. Phase-locked and time averaged 2D
Particle image Velocimetry (PIV) was used to study the dynamic characteristics of the flow.
The flow field shows that two different modes could be excited depending on nozzle
characteristic. The flapping mode was associated with alternate shedding of vortices. This
introduces strong steering of the jet to one side or the other. Turbulence, Jet spread and
entrainment characteristics were far more superior to the non-flapping or a pulsed jet. The
second mode which was a non-flapping mode is associated with the formation of a counter
rotating vortex pair. The turbulence associated with both these modes was convected along
with the vortical structure in the flow. The jet vortices formed by the self-excited flow were
not just convected by the flow, but these determined the flow field and mixing characteristics
of the jet.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
液体流体中流速检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Two-phase annular flow is commonly used in both commercial and industrial heat transfer; however, we do not yet possess a thorough understanding of the nature of the fluid. Most analytical annular two-phase models are based on a relationship between the
liquid film thickness, liquid film mass flux, and the axial pressure gradient or interfacial
shear stress. The film thickness calculated from these models can then be utilized to
determine the heat transfer coefficient of the flow. Although they are specific to certain
flow regimes and fluids, empirical models remain more accurate than these analytical
models. The key to understanding these flows lies with the liquid film. Therefore, to
better understand the pressure drop and heat transfer of annular two-phase flow, this
study involves the development of local, liquid velocity measurement techniques and
their application to horizontal, wavy-annular two-phase flow.
Two techniques, Bubble Streak Tracking (BST) and Thin Film Particle Image
Velocimetry (TFPIV), have been developed in this study. Utilizing naturally occurring
bubbles within the liquid film, the BST technique determines the liquid velocity by
measuring reflected light streaks from the bubbles. A three-colored LED array creates
directionally unambiguous streaks, while a strobe illuminates interfacial features that
affect the liquid velocity. The TFPIV technique applies a typical micro-PIV system to a
macroscopic flow with the addition of a non-trivial image processing algorithm. This
algorithm successfully overcomes the image noise that occurs when applying PIV to a
two-phase, thin film. Although difficulties arise when processing the BST data, the
results of the BST and TFPIV methods are comparable, making BST an economical
alternative to TFPIV for calculating liquid film velocities.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流速
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
气泡中分离,速度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Vortex generator jets (VGJs) have proven to be effective in minimizing the separation losses on low-pressure turbine blades at low Reynolds numbers. Experimental data collected using phase-locked particle image velocimetry and substantiated with a hot-film
anemometer were used to answer fundamental questions about the influence of VGJs on a separated boundary layer. The data were collected on the suction surface of the Pack B blade profile, which has a non-reattaching separation bubble beginning at 68% axial
chord. Two VGJ pulse histories were created with different frequencies, jet durations,and duty cycles. The mechanisms responsible for boundary layer separation control were
shown to be a combination of boundary layer transition and streamwise vortical structures. Jet duration and relaxation time were important VGJ characteristics in determining the extent of control. The unsteady environment characterisitic of the low-pressure turbine section in a gas turbine engine effectively reduces the time-averaged separation zone by as much as 35%. Upstream blade rows create unsteady flow disturbances (wakes) that transition the flow. This transitioned flow propagates downstream, re-attaching the separation bubbles on the subsequent blade row. Phase-locked PIV and hot-film measurements were used to document the characteristics of this separation zone when subjected to synchronized unsteady wakes and VGJs. The phase difference between VGJ actuation and the wake
passing, blowing ratio, and VGJ duration were optimized to achieve the greatest timeaveraged control of the separation zone. The experimental data were used to identify the important characteristics of the wake/jet interaction. Phase-locked PIV measurements were taken to isolate the wake event.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
分离,速度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
油水空气中关于油/水, 空气/水界面的过渡态研究检测方案(椭偏仪)
Insoluble monolayers at the air-water interface are exposed to a gas phase containing organic hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons are partly incorporated within the monolayer which leads to changes
in orientational order and the formation of new phases of different morphology. The transition state resembles features of the air-water and oil-water interface and the control of the hydrocarbon partial
pressure allows continous tuning between both interfaces. The phospholipid D,L-R-dipalmitoylphosphatidylethanolamine,DPPE, and an esterdiol hexadecanoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester, ESD-16, are used as amphiphiles, and pentane, n-hexane, cyclohexane, 2,2-dimethylbutane, n-heptane, n-decane, and n-dodecane are used as hydrocarbons. Both amphiphiles differ in their headgroup size. In DPPE the aliphatic tail determines the packing within the monolayer, but in the case of ESD-16 it is the headgroups.The structural changes are monitiored by surface pressure-area (ð,A) isotherms and imaging ellipsometry.The influence of the chemical nature of the hydrocarbon and the effect of the partial pressure of the
hydrocarbon on the monolayer structure are assessed.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
关于油/水, 空气/水界面的过渡态研究
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
界面中分子取向,精度和灵敏度分析检测方案(其它光谱仪)
Polarization null angle (PNA) method is an accurate alternative to the commonly used polarization intensity ratio method in
determination of molecular orientation at interfaces with sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy (SFG-VS). Here,
the accuracy and sensitivity of PNA method is tested on different experimental configurations. It is found that its accuracy and sensitivity
are more sensitive to the incident angle of the visible beam than the IR beam, and the range of the optimal experimental
configurations is identified. This development makes better understanding of the polarization measurement in SFG-VS, and should
find more applications for interface studies.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
分子取向,精度和灵敏度分析
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
水解离子,互补两性离子,可溶性表面活性剂,表面分子中反应动力学模拟,和频发生光谱学,SFG检测方案(其它光谱仪)
An aqueous ionic surfactant 1-dodecyl-4-dimethylaminopyridinium (DMP) bromide and the
corresponding zwitterion 2-(4-dimethylaminopyridinio)-dodecanoate (DPN) were explored
by means of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and, for the ionic system, by infraredvisible
sum frequency generation (IR-VIS SFG). The molecular structure of the interfacial
layer was investigated for the ionic and zwitterionic systems as a function of surfactant
concentration, both in water and in salt (KF or KBr) solutions, by MD simulations in a slab
geometry. The build up of the surface monolayer and a sublayer was monitored, and density
and orientational profiles of the surfactants were evaluated. The difference between the ionic
and zwitterionic systems and the effect of the added salt were analyzed at a molecular level.
The results of MD simulations were compared to those of nonlinear optical spectroscopy
measurements. Infrared visible sum frequency generation (IR-VIS SFG) was employed to
study the DMP ionic surfactant in water and upon addition of simple salts. The influence of
added salts on the different molecular moieties at the interface was quantified in detail
experimentally.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
反应动力学模拟,和频发生光谱学,SFG
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
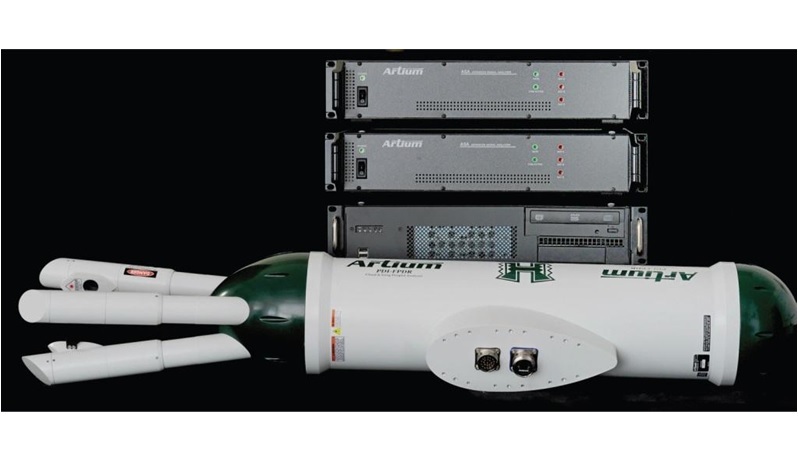
液滴中速度,粒径,惯性聚簇效应检测方案(干涉仪)
Water droplets are introduced via four spray nozzles,
with the resulting size distribution being quite broad
( ¯ d = 22 μm, ¾d = 13 μm). Downstream, a Phase Doppler
Interferometer (PDI) (15) simultaneously measures the
diameter (di), downstream speed (vi), and arrival time
(ti) of any droplets that traverse its view volume (which
has a linear dimension of roughly 150 μm). The PDI system
was built and calibrated by Artium Technologies, Inc.
and is designed for in situ measurement, such that the instrument
does not disturb the flow through the measurement
volume when aligned parallel to the mean flow.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度,粒径,惯性聚簇效应
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
碳烟中体积分数,初级粒径,温度场检测方案(烟气分析仪)
Laser-Induced Incandescence (LII) is investigated in laminar premixed flat ethylene/air flames at pressures up to 5 bar in a recently constructed high-pressure burner. Time-resolved LII signals were compared with a numerical model considering the influence of pressure on the LII signal decay. Peak particle temperatures after laser heatup were measured by the detection of the LII signal at two wavelenghts. Laser-induced emission spectra enabled to check for interfering signals. Gas-phase temperatures were requiered to compare the LII signal decay with the model and were measured using multi-line NO-LIF thermometry.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
体积分数,初级粒径,温度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
碳氢,湍流,火焰,多反应区中火焰前锋,自由基,羟基,速度场,浓度场检测方案(流量计)
Detection and imaging of multi-reaction zones is an essential tool for understanding the detailed structure
of complicated flames. In this work a combined 4-camera technique is presented for multi-reaction zones
imaging. The technique combines highly advanced laser-based diagnostics tools, namely Rayleigh scattering,
laser-induced predissociation fluorescence (LIPF) of OH, LIF of PAH, and LIF of formaldehyde (CH2O). The
application of this combined technique in turbulent non-homogeneous hydrocarbon flames is quite new. The
technique shows its ability to detect simultaneously rich, lean and diffusion reaction zones. The 3 reaction
zones can be spatially resolved, providing essential information about their interaction and overall flame
stability. Therefore, the detection and study of triple flame structures in non-homogeneous turbulent flames
becomes possible. An example of a triple flame structure in a turbulent lifted non-premixed methane flame
is presented. The present work proves that the developed technique is a powerful tool for multi-reaction
zone measurements in turbulent and laminar flames.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
火焰前锋,自由基,羟基,速度场,浓度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
火焰,氮氧化物中氮氧化物浓度检测方案(流量计)
Nitric oxide laser-induced-fluorescence (NO-LIF) 2-D imaging measurements using a new multi-spectral
detection strategy are reported for high-pressure flames (1–60 bar). This work builds on previous
research that identified interference LIF from O2 and CO2 in high-pressure flames and optimized the choice
of excitation strategies as a function of application conditions. In this study, design rules are presented to
optimize the LIF detection wavelengths for quantitative 2-D NO-LIF measurements over a wide range of
pressures (1–60 bar) and temperatures. Simultaneous detection of LIF in multiple wavelength regions
enables correction of the NO signal for interference from O2 and CO2 and allows simultaneous imaging
of all three species. New experiments of wavelength-resolved 1-D LIF in slightly lean (/ = 0.9) and slightly
rich (/ = 1.1) methane/air flames are used to evaluate the design rules and estimate the NO detection limits
for a wide range of flame conditions. The quantitative 2-D measurements of NO in the burnt gas are compared
with model calculations (using GRI-Mech 3.0) versus pressure for slightly lean and slightly rich
flames. The discussions and demonstrations reported in this study provide a practical guideline for application
of instantaneous 1-D or 2-D NO-LIF imaging strategies in high-pressure combustion systems.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
氮氧化物浓度
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
湍流火焰中热释放速率检测方案(流量计)
In this work, we report on the direct measurement of heat release rates via
simultaneous laser-induced fluorescence of OH and CH2O radicals using planar laserinduced
fluorescence (PLIF). The product of the two images is shown to correlate
with the forward production rate of the HCO radical, which in turn has been found to
correlate well with heat release rates in premixed hydrocarbon flames. Heat release
rate measurements were also taken with OH* for comparisons with the results from
the laser-based technique. The measurements were made in a lean turbulent premixed
flame subject to acoustic forcing; this flame mimics the instabilities encountered in
lean premixed pre-vaporized combustors (LPP). As the scheme is based on probing
radical species that participate in the major heat release reactions, it is the closest nonintrusive
measure of heat release rate currently available and thus presents a very
useful diagnostic tool in combustion research.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
热释放速率
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
燃气轮机,模型燃烧器,燃烧,合成气中速度场,浓度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
A parameter study was conducted to characterize the combustion of a hydrogen-rich syngas fuel in swirl-stabilized flames in a gas turbine model combustor with optical access. Three thermal power-loadings were tested and equivalence ratio was varied in a range of Φ ≈ 0.4 - 0.6 by changing the fuel flow rates at constant air flow.
Velocity, heat-release and flame zone shape were studied using optical diagnostics including PIV, OH-LIF and OH* chemiluminescence imaging. A main goal of this work was the establishment of an experimental data base for the validation of numerical simulations.
The syngas burned stably and without significant thermo-acoustic oscillations at all operating conditions. The inner recirculation zone is identified as a key stabilization mechanism for this burner. This is consistent with previous studies for syngas mixtures with a high CO content in the same burner. Changes in equivalence ratio and the thermal power of the flame had only a small impact on the overall flame shape and the burning behavior.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度场,浓度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
电致颗粒悬浮,可燃尘埃混合体中流场,速度场,速度矢量场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
The Electric Particulate Suspension (EPS) is a combustion ignition system being developed at Iowa State University for evaluating quenching effects of powders in microgravity (quenching distance, ignition energy, flammability limits). Because of the high cloud uniformity possible and its simplicity, the EPS method has potential for ‘benchmark’ design of quenching flames that would provide NASA and the scientific community with a new fire standard.
Microgravity is expected to increase suspension uniformity even further and extend combustion testing to higher concentrations (rich fuel limit) than is possible at normal gravity. Two new combustion parameters are being investigated with this new method: (1) the particle velocity distribution and (2) particle-oxidant slip velocity. Both walls and (inert) particles can be tested
as quenching media. The EPS method supports combustion modeling by providing accurate measurement of flame-quenching distance as a parameter in laminar flame theory as it closely relates to characteristic flame thickness and flame structure. Because of its design simplicity, EPS is suitable for testing on the International Space Station (ISS). Laser scans showing stratification effects at 1-g have been studied for different materials, aluminum, glass, and
copper. PTV/PIV and a leak hole sampling rig give particle velocity distribution with particle slip velocity evaluated using LDA. Sample quenching and ignition energy curves are given for aluminum powder. Testing is planned for the KC-135 and NASA’s two second drop tower.
Only 1-g ground-based data have been reported to date.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
流场,速度场,速度矢量场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
湍流边界层,聚合物,拖曳减阻中速度矢量场,浓度场检测方案(粒子图像测速)
Much progress has been made in the understanding of the phenomenon of drag reduction by dilute solutions of polymers since its discovery in 1948. While the use of advanced techniques in experiments and computational simulations have dramatically advanced
our understanding of the phenomenon, a complete and conclusive explanation of the physics associated with the phenomenon is still lacking. In particular, drag reduction in boundary layers with injection has not been studied extensively to understand the processes and physics that govern the spread and mixing of the injected polymer in the flow. To overcome this limitation, in the present work, drag reduction due to polymer injection in a turbulent boundary layer is studied using simultaneous Particle Imaging
Velocimetry (PIV) and Planar Laser Induced Fluorescence (PLIF). PIV is used to measure the velocity of the flow in the boundary layer and to calculate higher order velocity statistics. PLIF
is used to study the distribution and spread of the injected polymer in the boundary layer by tracking a fluorescent dye mixed in with it. The polymer of choice, polyethylene oxide, is injected as a dilute solution into a fully turbulent Newtonian boundary layer and measurements of velocity and concentration are made at different downstream locations on the flat plate to study the effect of the polymer on the flow and the evolution of drag reduction. The data from the two measurement techniques are combined to calculate turbulent fluxes and to estimate the turbulent Schmidt number in polymer drag reduced flows.
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
速度矢量场,浓度场
北京欧兰科技发展有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
填料中样品检测检测方案(色谱配件)
近期华人抗体协会发布一篇文章介绍到连续制造工艺被FDA推崇备至:连续制造工艺基于其稳定高效率的优势,已经在其它许多行业成为极其成功的生产模型。然而很长一段时间以来,制药行业以严格监管和法规要求过于保守而被行业所诟病,故多数仍以批次生产为主。近年来,随着业界对于产能效率和生产成本的不断重视,生物制药行业对于连续工艺的关注度也在不断增加,希望能借以提高生产效率和设备利用率,且已有案例表明特定连续技术整合到现有生物药生产流程后,显现了诸多优势。作为全球药物监管的领先者,FDA一直是连续制造工艺的有力倡导者。早在2017年,FDA就发布了关于连续制造(Continues manufacturing, CM)的意见征求稿;2018年FDA 向三个连续制造项目提供近六百万美元资金,旨在帮助实施创新技术以提高产品质量并实现行业现代化;2019年2月26日,FDA颁布了涉及CM的关键指南草案《Quality Considerations for Continuous Manufacturing》,必将对此技术的推动起到巨大作用,同时FDA 局长 Scott Gottlieb 和药品中心主任 Janet Woodcock 也为CM高调站台,在随指南发布的声明中一再强调连续制造的优势,由此看来CM未来或许已不远。令人高兴的是,得益于纳微科技在纳米材料及键合等多方面取得的突破性进展,UniMab Protein A亲和层析介质因其诸多独有领先优势而特别适合用于连续柱色谱体系。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
样品检测
苏州纳微科技股份有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
气相色谱中分析方法建立检测方案
在实际工作中,当我们拿到一个样品,我们该怎样定性和定量,建立一套完整的分析方法是关键,下面介绍一些常规的步骤:
1、样品的来源和预处理方法
GC能直接分析的样品通常是气体或液体,固体样品在分析前应当溶解在适当的溶剂中,而且还要保证样品中不含GC不能分析的组分(如无机盐),可能会损坏色谱柱的组分。这样,我们在接到一个未知样品时,就必须了解的来源,从而估计样品可能含有的组分,以及样品的沸点范围。如果样品体系简单,试样组分可汽化则可直接分析。如果样品中有不能用GC直接分析的组分,或样品浓度太低,就必须进行必要的预处理,如采用吸附、解析、萃取、浓缩、稀释、提纯、衍生化等方法处理样品。
检测样品:
其他
检测项:
分析方法建立
浙江爱吉仁科技股份有限公司
查看联系电话
前往展位
仪器信息网行业应用栏目为您提供2271篇其他检测方案,可分别用于,参考标准主要有等